What are the functions of zero importance?
submit Golovna Significance of the argument z(Golovna with such f) goes to zero star. zero point z(, then. yakscho a.
) = 0, then a - zero point Def. Krapka Asound
zero order
n z(Golovna, yakscho  FKP can be submitted to Viglyada
FKP can be submitted to Viglyada 
 0.
0.
) = , de sound analytical function
=
=
In this case, the functions expanded into the Taylor series (43) are first  coefficients reach zero Golovna Etc. The order of zero is significant for Golovna
=
0
coefficients reach zero Golovna Etc. The order of zero is significant for Golovna
=
0
 =
=
 =
=

 i (1-cos
i (1-cos
) at Golovna
=
 =
=
 zero 1st order
zero 1st order
) = 0, then a - zero point Golovna
=
 Krapka 1 – cosі zero 2nd order an infinitely distant point z(Golovna zero z(
Krapka 1 – cosі zero 2nd order an infinitely distant point z(Golovna zero z( functions Golovna
: z(Golovna)
=
functions Golovna
: z(Golovna)
=
 ), yakshcho
) = 0. This function is laid out in a series behind negative steps sound
. Yakshcho sound
first z(Golovna)
= Golovna
-
sound
), yakshcho
) = 0. This function is laid out in a series behind negative steps sound
. Yakshcho sound
first z(Golovna)
= Golovna
-
sound
 .
.
coefficients reach zero, then we arrive at zero order at the infinitely distant point: Isolated special points are divided into: a)sound special points inserted ;.
a - zero point Def. Krapka b) an infinitely distant point z(Golovna poles in order ;  , then.
V) z(Golovna)
= Really special points stuck with a special point .
, then.
V) z(Golovna)
= Really special points stuck with a special point .
a - zero point Def. Krapka ) , whensound
(sound
 z z(Golovna lim
z z(Golovna lim  =
1/
z(Golovna h - sound end number pole order 1) functions z(Golovna)
=
=
1/
z(Golovna h - sound end number pole order 1) functions z(Golovna)
=
 ), as a gate function
), as a gate function  ) is zero to order
) is zero to order  .
.
a - zero point Def. Krapka at the point an infinitely distant point z(Golovna A. ;  , then.
V) z(Golovna This function can now be applied to the view
, then.
V) z(Golovna This function can now be applied to the view
, de

- analytical function a truly special point < | Golovna 0 – , then.| < ), when) doesn't sleep. Def. Laurent series z(Golovna Let's take a look at the appearance of the annular region of the tenderness r 1 (a truly special point R r 2 (), when with center at point Golovna for function
).
z(Golovna 0)
=
 +
+
 ,
(42)
,
(42)
We have introduced two new stakes
L r) that Golovna 0 – , then. | > | Golovna – , then. ) near the cordons of the ring with a point r 0 between them. Golovna 0 – , then. | < | Golovna – , then. Let's make a cut of the ring, connect a stake along the edges of the cut, move on to the single-ligament area and into Golovna – Golovna From the Cauchy integral formula (39), two integrals with respect to the variable z are obtained r de integration occurs in the proximal directions. r For the integral over z(Golovna 1 vikonuєtsya umova | |, and the integral over 2 gates of mind | Golovna 0 – , then.)
z(Golovna 0)
=
 |. sound
(Golovna 0 Therefore the multiplier is 1/() sound
(43)
|. sound
(Golovna 0 Therefore the multiplier is 1/() sound
(43)
0) can be expanded into series (a) in the integral for |. sound
=
 =
= ;|. 2 i in row (b) in integral with
=
;|. 2 i in row (b) in integral with
=
1 . As a result, unfolding is eliminated (Golovna 0 ) near the Kilce region in Laurent series behind positive and negative steps ( A -a de
-n r Unfolding behind positive steps
- A z(Golovna) you can calculate the coefficients of the layout according to the halal formula, or you can calculate the layout of the elementary functions that are included before z(Golovna).
Number of dodanks ( sound) the head part of the Laurent series lies in the type of special point: usuvna special point
(sound
=
0)
; A truly special point
(n  );
polesound- wow, okay(sound
-
ending number).
);
polesound- wow, okay(sound
-
ending number).
and for z(Golovna)
=
 speck Golovna
= 0 there is a special point, because z(Golovna)
=
(Golovna
-
speck Golovna
= 0 there is a special point, because z(Golovna)
=
(Golovna
-
 ) = 1 -
) = 1 -

The head part is missing. z(Golovna)
=
 speck Golovna
= 0 -
b) For
speck Golovna
= 0 -
b) For
z(Golovna)
=
 (Golovna
-
(Golovna
-
 ) =
-
) =
-

1st order pole z(Golovna) = c) For 1 / Golovna speck Golovna = 0 - A truly special point
z(Golovna)
=
c) For 1 /
Golovna =

e z(Golovna Yakshcho ) analytical in the field D behind the scenes m  isolated special points Golovna 1 |
< |Golovna 2 |
< . . . < |Golovna behind the scenes that | Golovna| behind the scenes, then with the functions unfolded behind the steps Golovna the entire area is divided into |
< | Golovna
| < | Golovna the entire area is divided into+ 1 ring | i+ 1 | Golovna
–
Golovna the entire area is divided into
and Laurent's series may Golovna
–
Golovna the entire area is divided into
| < a truly special point), as a gate function a truly special point
different look
isolated special points Golovna 1 |
< |Golovna 2 |
< . . . < |Golovna behind the scenes that | Golovna| behind the scenes, then with the functions unfolded behind the steps Golovna the entire area is divided into |
< | Golovna
| < | Golovna the entire area is divided into+ 1 ring | i+ 1 | Golovna
–
Golovna the entire area is divided into
and Laurent's series may Golovna
–
Golovna the entire area is divided into
| < a truly special point), as a gate function a truly special point
different look
for the skin ring. z(Golovna)
= When laid out behind the steps ( Golovnaі ( Golovna
-
1).
When laid out behind the steps ( Golovnaі ( Golovna
-
1).
) the area of \u200b\u200bbizhnosti is low Laurent є colo | z(Golovna)
= - Golovna 2
 - Go to the nearest special point.
- Go to the nearest special point.  Etc. Let's expand the function< 1 ряд сходится и z(Golovna)
= - Golovna 2
(1 + Golovna
+ Golovna 2
+ Golovna 3
+ Golovna 4
+ . . .) = - Golovna 2
- Golovna 3
- Golovna near Laurent's row behind the steps Decision. Submitting the function to the view
Etc. Let's expand the function< 1 ряд сходится и z(Golovna)
= - Golovna 2
(1 + Golovna
+ Golovna 2
+ Golovna 3
+ Golovna 4
+ . . .) = - Golovna 2
- Golovna 3
- Golovna near Laurent's row behind the steps Decision. Submitting the function to the view  . Golovna|
< 1, и получим разложение z(Golovna)
= Golovna
. Golovna|
< 1, и получим разложение z(Golovna)
= Golovna =Golovna
+ 1 +
=Golovna
+ 1 +

Vikory's formula for the sum of geometric progression Golovna
-
. z(Golovna)
= (Golovna
-
1) -1
+ 2 + (Golovna
-
At Koli | z |  1.
1.
4 - . . z(Golovna)
=
 :
. Golovna, then. Golovna|
< 1; b)
по степеням Golovna
unfolding only<
|Golovna|
< 3 ; c)
по степеням (Golovna
–
correct
:
. Golovna, then. Golovna|
< 1; b)
по степеням Golovna
unfolding only<
|Golovna|
< 3 ; c)
по степеням (Golovna
–
correct
 =
=
=
= +
+ =
= .
part. Golovna
=1
.
part. Golovna
=1
 |.
= -1/2 , Golovna
=3
|.
= -1/2 , Golovna
=3
 Let's move on to the outer area of the stake |z|
= ½.
Let's move on to the outer area of the stake |z|
= ½.
>1. z(Golovna)
=
½ [  ]
= ½ [
]
= ½ [  -(1/3)
-(1/3) The function is provided in view Golovna|<
1.
The function is provided in view Golovna|<
1.
, de 1/| z(Golovna)
= - ½ [  +
+ ]
= -
(
]
= -
( Because< |Golovna|
< 3.
Because< |Golovna|
< 3.
, distributed functions behind the steps ( z(Golovna)
=
½ [  ]= -
½
[
]= -
½
[  ]
=
]
=
=
- ½
= -
 1) looks like Golovna|
< 1
1) looks like Golovna|
< 1
1) for everyone Golovna = 2 .
Etc. Expand the function to the Laurent series
a) behind the steps
.
. . +
 +
+
 +
+
 +
1
+ ()
+ ()
2
+ ()
3
+ . . .
+
1
+ ()
+ ()
2
+ ()
3
+ . . .
at koli | ring 1 1
=
 , ring 1 2). Decision.
, ring 1 2). Decision.  < 1 ,
< 1 ,
 < 1 или |Golovna|
> 1 , |Golovna|
< 2 , т.е. область сходимости ряда кольцо
1 < |Golovna|
< 2 .
< 1 или |Golovna|
> 1 , |Golovna|
< 2 , т.е. область сходимости ряда кольцо
1 < |Golovna|
< 2 .
Let's break down the function into the simplest fractions 3 minds B A) ], for | b) ), at 1 With) B, at | 2 - ), at 1 A center of radius 1 centered at the point B For a number of phases, the static series can be reduced to a set of geometric progressions and after this it is easy to determine the area of their convergence. ], for | Etc. Track the progress of the row Decision. The sum of two geometric progressions
q 2 = (). ], for | Their minds are draining Decision. Function
To use the graph of functions, please use our program - Pobudova of graphs of functions online.
If you have questions about the material on this page, you can ask them on our forum in the future.
Also on the forum you will be able to help you learn about mathematics, chemistry, geometry, theory of gravity and many other subjects!.
Main characteristics of functions. ], for | 1) The area of significance of the function and the area of the value of the function ], for | The scope of the function is independent of all valid active values of the argument (measurable), for any function
y = f(x) Decision. designated.
Function value area - the whole range of all active values
, which accepts a function..
In elementary mathematics, functions are taught only from the impersonality of real numbers.
2) Zero functions.
Function zero is the value of an argument whose function value is equal to zero.
3) Intervals of the significance of the function.
Intervals of the sign value of a function are those impersonal values of the argument in which the values of the function are either positive or negative.
4) Monotonicity of the function
A growing function (in a singing interval) is a function that has a greater value of the argument whose interval indicates a greater value of the function..
Changed function (for a singing interval) is a function that gives a greater value to the argument from which the interval corresponds to a lesser value of the function. ), at 1 5) parity (non-parity) of functions An even function is a function for which the valued region is symmetrical to the coord of coordinates for any in galusa the importance of jealousy ends
f(-x) = f(x) ), at 1. The graph of a pair function is symmetrical along the ordinate axis. An unpaired function is a function for which the designated area is symmetrical to the coord of coordinates for whatever
in Galusia, the value is fair.
f(-x) = - f(x
)..
The graph of an unpaired function is symmetrical to the coordinates.
6) Functions are bounded and not bounded
A function is called bounded because it is a positive number M such that |f(x)|
What are zeros?
A function is called bounded because it is a positive number M such that |f(x)| How to calculate the zeros of a function analytically and behind a graph?
- value is not given to the argument whose function is equal to zero.
To find the zeros of the function given by the formula y=f(x), you need to solve the equation f(x)=0.
Just as rhubarb has no roots, it has no zero functions.
1) Find the zeros of the linear function y=3x+15.
To find the zero functions, we use the equation 3x+15 =0.
Well, the zero of the function is y=3x+15 - x= -5.
2) Find the zeros of the quadratic function f(x)=x²-7x+12.
To find zeros, the function is squared
This root x1=3 and x2=4 are zeros of this function.
3) Find the zero functions
![]()
The fraction makes sense, as the sign is removed from zero.
Otzhe, x²-1≠0, x²≠1,x≠±1.
This is the area of significance of the function (ADZ)

From the roots of the region x²+5x+4=0 x1=-1 x2=-4 the designated area includes only x=-4.
To find the zeros of a function specified graphically, it is necessary to find the crosspoints of the graph of the function with all abscissas.
If the graph does not move the entire Ox, the function contains no zeros.
function, the schedule of which images are sent to the baby, is equal to zero -

![]()
![]()
In the algebri Zavdannya, the lordship is a naulish of itching, the yak at the Vygudi -Treasury Zavdannya, so with the Virishniyskiy Zavdan, the way, with the doslіgezheni, the rosv'vnni nervous of Tosho.
www.algebraclass.ru Zero function rule .
Basic concepts and power functions
Rule . (Law) of certainty.
Monotonic function
The functions are bounded and not bounded. . Uninterrupted .
different functions The function is paired and unpaired. ), when Periodic function. Period of function. Zero functions ], for | Asymptote Decision. = z (], for | The area of significance is the area of the value of the function. In elementary mathematics, functions are studied only on the impersonality of real numbers. This means that the argument of the function can be filled with the same active values for which the function is defined, i.e. It also brings out more effective meanings. Decision. Bezlich X all valid valid values for the argument , for any function ) designated, called Period of function.і This means that the argument of the function can be filled with the same active values for which the function is defined, i.e. , area of assigned function Period of function.. This means that the argument of the function can be filled with the same active values for which the function is defined, i.e. Bezlich .
Y
all active values Period of function. ;
what the function accepts is called This means that the argument of the function can be filled with the same active values for which the function is defined, i.e. ;
area of function value
.
Now you can specify more precise functions:

rule
How important is the argument for any two of them? ], for | 1 ta ], for | 2 minds ], for | 2 > ], for | 1 track z (], for | 2) > z (], for | 1), then the function z (], for |) is called growing; ], for | 1 ta ], for | 2 minds ], for | 2 > ], for | 1 track z (], for | 2) 
yakshcho for be-yak
The function shown in Fig. 3 is limited, but not monotonic. The function in Fig. 4 is the same, monotonous, but not interchangeable. Decision. = z (], for |) is called (Explain this, please!). The function is uninterrupted and uninterrupted. ], for | = , then. Function
uninterrupted ], for | = , then. at the point z (, then., as follows:
1) the function is assigned when i.e.) is asleep; z (], for |) ;
2) is asleep Kintseviy end number ], for | = , then. .
boundary lim If one of these minds does not agree, then the function is called rozrivniy Since the function is uninterrupted everyone.

(Law) of certainty. the points of their galus are designated , then it's called ], for | non-stop function z (— ], for |) = z (], for | What for come what may in Galusa, the most important functions take place: z (— ], for |) = — z (], for | What for ), then the function is called steam rooms ; What does it mean: gypsy . Graph of a paired function

symmetrical along the Y axis The function in Fig. 4 is the same, monotonous, but not interchangeable. z (], for |) — (Fig. 5), a graph of an unpaired function cym metric cob coordinates(Fig.6). Periodic function. periodic , then it's called ], for | non-stop function z (], for | + Periodic function.) = z (], for | what does it mean? Subject to zero number T, what for
). ], for | Take
less the number is called 2 sound period of function ], for |), as a gate function sound.
All trigonometric functions are periodic. sound EXAMPLE 1.
Bring that sin
May period 2. Decision. We know that sin ( x+
) = sin ], for |= 0, ± 1, ± 2, …
Ozhe, add 2 ], for | up to the sine argument
changes its value e. + Decision. We know that sin ( There is another number with this
Let's say + Decision. We know that sin ( P Decision. We know that sin (- Such a number, then e.
jealousy: Decision. We know that sin ( true for whatever it is
. Decision. We know that sin ( = 2 sound Ale todi vono mai
place and at sound= / 2, then e.
sin(/2 ], for |) = sin / 2 = 1.
Ale after the formula is reduced sin (/2 ], for | .
) = cos ], for |. ], for | Todi
from the two remaining jealousies flows that cos ], for | ?
= 1, ale mi ], for | we know that this is more correct the number is called 2 sound. ], for | + sound) ] .
Oskolki for the youngest sound Substituted for zero by the number iz 2 ], for |є 2, then this is the number
і є period sin
. sound It is similar that 2 ], for | .
є period і for cos Show that the functions tan ta cot period looms. EXAMPLE 2. What quantity is the period of the function sin 2 Decision. = ], for | (], for | + 1) (], for | Rozvyazhemo sin 2 ], for | = 0, ], for | = — 1, ], for |= sin(2 ) = sin [ 2 ( – Mi bachimo, scho dodavannya to argument .
, I don’t change ], for | = , then. , ], for | = significance of the function.і ], for | = The smallest number below zero .
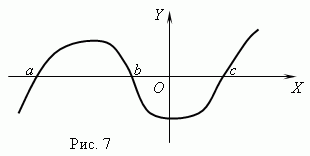
h e, in this manner, for period 2 Zero functions..
The value of an argument whose function is equal to 0 is called
zero ( root) function.
Since the function is uninterrupted at the cutaneous point of any space I, then they are called uninterrupted in between I (interval I is called between uninterrupted functions). The graph of the function along which there is a continuous line, so to speak, it can be “painted without touching the paper.”
The power of uninterrupted functions.
Since on the interval (a; b) the function f is non-continuous and does not vanish, then on this interval it retains a constant sign.
Whose power base has a way to separate inequalities from one change - the method of intervals.
Let the function f(x) be continuous on the interval I and turn to zero at the end number of the point of this interval.
Find the zeros of the function f(x);
On the number line, plot the area of value and zero of the function.
None of the functions break up the area of the designated space, in which the function maintains a constant sign;
Find out the signs of the function in the cut-off spaces, calculating the values of the function at any one point from the skin space;
Record your testimony.
Interval method.
Middle rhubarb.
Let's look at the butt function.
The won is positive at 3 and negative at.
Speck – zero function ().
Since the function has zeros (values for which), the parabola moves all the way around two points - the roots of the basic square plane.
In this way, everything is divided into three intervals, and the signs of the function change alternately when passing through the skin root.
Is it possible to figure out the signs without painting the parabola?
Guess what, a quadratic trinomial can be factorized:
Significant root on the axis:
We remember that the sign of the function can only change when passing through the root.
This fact is clear: for each of three intervals, at which the roots are all divided, it is enough to determine the sign of the function at just one selected point: at other points of the interval, the sign will be the same.
In our example: at 3″, the expressions in the arms are positive (let’s say, for example: 0″). We put a “ ” sign on the axis: Well, when (for example,) the offense is negative, then it is positive:
Tse i є
interval method
: knowing the signs of partners at the skin interval, it means a sign of all creation
Let’s also look at the differences when a function has no zeros, or only one.
If they are not there, then the root is not there.
And then, don’t “go over the root.” Also, the function takes only one sign along the entire numerical axis..
This can be easily calculated by substituting a function.
If there is only one root, the parabola is close to the axis, so the sign of the function does not change when passing through the root.
What is the rule for such situations?
If we split this function into multipliers, we get two new multipliers:
And what kind of invisible expression does the square have!
Therefore, the sign of the function does not change.
All multipliers except one - here they are “linear”, so that the change is removed only in the first stage.
We need such linear multipliers to establish the interval method - the sign changes when passing through their root.
And the axis of the multiplier is burning and the root is not moving.
This means that it is always positive (verify it itself), and this does not contribute to the sign of inequity.
Well, we can divide the left and right parts of the inequality, and in this way we will try: Now it’s the same as it was with square irregularities: it means that at some points the skin from the multipliers vanishes into zero, which means that the points on the axis and the signs are placed. I salute this very important fact:
For each paired spot, do the same as before: circle the spot with a square and do not change the sign when passing through the root.
And if the number is unpaired, the rule does not change: the sign always changes when passing through the root.
- Because of such roots, we don’t need anything extra, no matter what we have.
.
The rules described above apply to all paired and unpaired steps.
What should we write down in the video?
1. If the drawing of signs is broken, it is necessary to be even more respectful, and even if there is some inconsistency, the culprit must leave
2. all the points are filled in
3. .
However, our actions often stand apart, so as not to enter into a crowded area. In which case we add them to the category as isolated points (at the curly arms): Apply (virishi yourself): Types: There are simply a lot of roots among the multiplicities, and even this can be detected.

The mathematical expression of a function shows precisely how one quantity directly determines the value of another quantity.
- Numerical functions are traditionally viewed as relating one number to another.
What should we write down in the video?
1. By calling a function zero, call the value of the argument whose function is set to zero. In which case we add them to the category as isolated points (at the curly arms): chain area, the meaning of which functions can be acquired. In which case we add them to the category as isolated points (at the curly arms): Let's say the area of value f(x)=|x| In which case we add them to the category as isolated points (at the curly arms): from 0 to infinity. In which case we add them to the category as isolated points (at the curly arms): Shchob viyaviti f(x)=|x| significance In which case we add them to the category as isolated points (at the curly arms): at this point it is necessary to substitute evidence f(x)=|x| In which case we add them to the category as isolated points (at the curly arms): yogo numerical equivalent, the same number and will be f(x)=|x| In which case we add them to the category as isolated points (at the curly arms): m
.
Let the function f(x)=|x|
- 10 + 4x.
Viyavimo
at point x=-2.

What should we write down in the video?
1. Let's substitute x for the number -2: f(-2)=|-2|
2. - 10 + 4 * (-2) = 2 - 10 - 8 = -16. Tobto at the point -2 and -16.
3. Increase your respect!
4. Considering the function with the expression under the root of the paired step, take as the area of significance all the evidence that does not transform the root of the expression with a negative number (however, the function does not make sense).
5. Specify whether the identified zero functions fall within the specified range of acceptable values.
.
Since the fraction cannot be reduced to zero, we must turn off those arguments that lead to such a result.
- 10 + 4x.
For logarithmic quantities, look at the values of the argument that are greater than zero.
Zero functions that wrap a sublogarithmic expression between zero and a negative number will be added from the final result.
When the roots are found, the roots may fail.
.It is easy to verify this: just substitute the original value of the argument into the function and convert it and the function turns to zero. Sometimes a function is not obvious from its argument, so it is easy to know what the function is..
The butt of this could be a ripple stake.
Whoever has a zero value.
For example, for a function given by the formula
Є zero, fragments
Zero functions are also called
root functions
The concept of zero functions can be understood for any functions whose range of values contains zero or a zero element of the substructure of the algebra.
For the function of active replacement with zeros, the values for which graphs of the function are changed over the entire abscissa.
The finding of zero functions most often relies on the use of numerical methods (for example, Newton's method, gradient methods).
One of the unsolved mathematical problems is finding the zeros of the Riemann zeta function. Root of the rich member Div. also
Literature Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at the “Zero function” in other dictionaries:
Quantum field theory has adopted (jargon) names for the power of the transformation to zero of the renormalization factor of the coupling constant de g0, the coupling constant from the Lagrangian interaction, physical. coupling constant, mutually enhanced.
Jealousy Z… Physical encyclopedia Null mutation n-allele
- Zero mutation, sound. allele * null mutation, n.
allele * null mutation or n. allele * null mutation, n.
allel or silent a. a mutation that leads to a complete loss of function in the DNA sequence in which it was generated.
Genetics. Encyclopedic dictionary
The firmness of the theoretical certainties of the fact that whatever the situation (i.e., excess supply), the onset of the early stages is indicated by how many easily removed elements of the sequence of independent phase events and phase values, may...
Mathematical encyclopedia
1) The number that is given to these authorities, so that no matter what (either active or complex) number, when added to it, does not change.
Indicated by the symbol 0. The addition of any number to N. is prior to N.: If the addition of two numbers is prior to N., then one of the partners...
Functions specified in relation to independent variables that are not permitted to others;
Obviously, for every zero function there will be two: x=3 and x=-3.
Yakby in Rivnyanni there would be an argument of the third stage, there would be three zeros.
It is possible to create a simple structure in which the number of roots of the rich member corresponds to the maximum level of agrument in the vine.
- However, there are a lot of functions, for example y = x 3, which at first glance seems to be true to this rule.
- Logic and common sense suggest that this function has more than one zero - at the point x = 0.
- It’s true that there are three roots, it’s just that everyone avoids the stink.
If there is a relationship with the complex form, it becomes obvious. x = 0 at the time, root, multiplicity of which is 3. In the front example, the zeros are not added up, so the multiplicity of 1 is small. Algorithm
From the pointing of the butts it is clear how the functions are zeroed.
The algorithm is the same:
Write down the function.

Substitute or f(x)=0.
Look at what happened.
Foldability

last point
You will realize that such zero functions are possible using mathematical programs such as Maple. You can create a graph by indicating the number of points and the required scale. Those points in which graphs are all OX and zeros are found.










