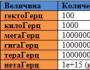
Ethernet and Fast Ethernet setup. Fast Ethernet Technology Understanding Active Monitor Functions in LOM Token Ring
The widest range of standard Ethernet tethers is the Ethernet tether. Vaughn appeared in 1972 rock, and in 1985 rock became the international standard. Її accepted by the largest international organizations for standards: Committee 802 IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers) and ECMA (European Computer Manufacturers Association).
The standard is called IEEE 802.3 (read in English as "eight oh two dot three"). Vіn assigns multiple access to a mono channel type bus with conflict detection and transmission control, so with a CSMA / CD access method, which is already a guess.
The main characteristics of the cob standard IEEE 802.3:
Topology - bus;
· Transmission medium - coaxial cable;
· Transmission speed - 10 Mb/s;
· the maximum length of the merezha is 5 km;
· maximum number of subscribers – up to 1024;
· Dovzhina segment merezhі - up to 500 m;
· Number of subscribers per segment - up to 100;
· Access method - CSMA / CD;
· Vuzkosmugov transmission, without modulation (monochannel).
Strictly seeming, between IEEE 802.3 and Ethernet standards, there are some insignificant details, but you should not guess about them.
The Ethernet network is currently the most popular in the world (more than 90% of the market), it is possible that such a won and be lost in the nearest future. What a significant world was taken by those who, from the very beginning of the characteristics, parameters, protocols of the measures, were recognized, after which the great number of virobniks in the world began to launch Ethernet equipment, as I will sum up among myself.
The classic Ethernet cable has a 50-ohm coaxial cable of two types (thin and thin). However, in the last hour (since the beginning of the 90s) the largest version of Ethernet appeared, as a victorious as the medium of transmission of twisted bets. A standard has also been drawn up for laying in a fiber optic cable. For vakhuvannya tsikh zmin to cob standard IEEE 802.3 was zrobleno vіdpovіdnі dаvannya. In 1995, a new standard appeared for a larger version of Ethernet, which works on a speed of 100 Mbit / s (the so-called Fast Ethernet, IEEE 802.3u standard), which is twisted like a transmission medium, or a fiber optic cable. In 1997, a 1000 Mbit/s version was released (Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE 802.3z standard).
The standard topology bus daedal is more widely used topology type passive star and passive tree. At the same time, the number of repeaters and repeater concentrators are transmitted, which can be obtained among themselves by different parts (segments) of the merezhi. As a result, a tree-like structure can be formed on segments of various types (Fig. 7.1).
Like a segment (parts of a merezhі) can be a classic bus or a single subscriber. For bus segments, a coaxial cable is used, and for changing a passive star (for connecting to a single computer hub), a pair of fiber optic cables is twisted. The main thing is to take away topology from the beginning - sob it has closed paths (loops). In fact, to get out, that all subscribers are connected to the physical bus, so the signal from the skin to them expands on all sides and does not turn back (like in the ring).
The maximum length of the wire cable in general (maximum signal path) theoretically can reach 6.5 km, but practically does not exceed 3.5 km.
Rice. 7.1. Classic Ethernet network topology.
At the Fast Ethernet network, the physical topology of the bus is not transferred, only a passive star or a passive tree is chosen. Before that, Fast Ethernet has a lot of zhorstkіshі vomogi to the boundary line of the border. Even with a 10-fold increase in the speed of transmission and saving the format of the package, the minimal cost becomes ten times shorter. In this way, the value of the subway hour of the signal passing by the measure changes for 10 times (5.12 µs versus 51.2 µs Ethernet).
For transmission in an Ethernet network, the standard Manchester code is used.
Access to the Ethernet network is controlled by the CSMA/CD vipadkovym method, which ensures the equality of subscribers. At the merezha, there are packages of changeable dozhina.
For an Ethernet network, which operates at a speed of 10 Mb/s, the standard defines the following main types of segments in the network, oriented to different media of transmission of information:
10BASE5 (common coaxial cable);
· 10BASE2 (thin coaxial cable);
10BASE-T (vita pair);
· 10BASE-FL (fiber optic cable).
The name of the segment includes three elements: the number "10" means the speed of transmission of 10 Mbit / s, the word BASE - transmission to the main frequency mix (that is, without modulating the high-frequency signal), and the remaining element - the allowable length of the segment: "5" - 500 meters, " 2" - 200 meters (more precisely, 185 meters) or the type of connection line: "T" - twisted pair (English "twisted-pair"), "F" - fiber optic cable (English "fiber optic").
So for the Ethernet network itself, which works on the speed of 100 Mbit / s (Fast Ethernet), the standard defines three types of segments, which are considered by the types of transmission medium:
· 100BASE-T4 (quadruple twisted pair);
· 100BASE-TX (double twisted pair);
· 100BASE-FX (fiber optic cable).
Here the number "100" means the speed of transmission of 100 Mbit / s, the letter "T" - a twisted pair, the letter "F" - a fiber optic cable. Types 100BASE-TX and 100BASE-FX can sometimes be combined under the names of 100BASE-X, and 100BASE-T4 and 100BASE-TX - under the names of 100BASE-T.
Merezha Token-Ring
The Token-Ring (marker ring) was propagated by IBM in 1985 (the first version appeared in 1980). The won was assigned to the union of all types of IBM computers. Even though the fact that I support IBM, the largest manufacturer of computer technology, to talk about those who need to add special respect. But not less important are those that Token-Ring is in Denmark the international standard IEEE 802.5 (although Token-Ring and IEEE 802.5 are insignificant). Tse to put tsyu merezh odnієyu rіven per status z Ethernet.
The development of Token-Ring is a great alternative to Ethernet. If you want Ethernet to close the network at once, Token-Ring cannot be used hopelessly old. Over 10 million computers in the whole world are united by a network.
Merezha Token-Ring may be a ring, wanting to call it out more guess the sky. For this reason, some subscribers (computers) do not come to the measure without intermediary, but through special concentrators for rich station access (MSAU and MAU - Multistation Access Unit). Physically, the mesh establishes a mirror-kilce topology (Fig. 7.3). In fact, the subscribers are united all the same in the ring, so that from them they transmit information to one land subscriber, and receive information from another.

Rice. 7.3. Zirkovo-kiltseva topology of the Token-Ring network.
As the medium of transmission in the IBM Token-Ring line, a twisted pair of unscreened (UTP) and screened (STP) pairs were interlocked, and then there were options for equipment for a coaxial cable, as well as for a fiber optic cable in the FDDI standard.
The main technical characteristics of the classic Token-Ring variant:
· Maximum number of concentrators type IBM 8228 MAU - 12;
· the maximum number of subscribers for the Merezha is 96;
· the maximum length of the cable between the subscriber and the concentrator is 45 meters;
· maximum cable length between concentrators – 45 meters;
· the maximum length of the cable, which connects all concentrators - 120 meters;
· Speed of data transmission – 4 Mb/s and 16 Mb/s.
The necessary characteristics can be seen up to the point where the odds of non-screened twists of the bet are reversed. Even though the middle of the transmission is victorious, the characteristics of the border can be changed. For example, with a different screened twisted bet (STP), the number of subscribers can be increased to 260 (zam_st 96), the cable length - up to 100 meters (zam_st 45), the number of concentrators - up to 33, and the number of concentrators - up to 20 concentrators meters Fiber optic cable allows you to extend the length of the cable up to two kilometers.
For transmission in the Token-Ring, a biphasic code is required (more precisely, this option with a binding transition at the center of the bit interval). As in the be-yakіy zirkopodіbnіbnіy topologii, zhdnih dodatkovyh zahodo elektricheskogo uzhodzhennia that zіrkopodіbnіy zemlіnії іn't nebіbіl. Uzgodzhennya vykonuetsya equipment mesh adapters and concentrators.
For the connection of Token-Ring cables, RJ-45 roses are used (for non-screened twisted bets), as well as MIC and DB9P. Conducting at the cable, one-time contacts of roses are connected (this is why "straight" cables are called so).
Merezha Token-Ring in the classic version comes with Ethernet merezha both for the allowable size and for the maximum number of subscribers. Depending on the speed of transmission, then in Denmark there are versions of Token-Ring for 100 Mb/s (High Speed Token-Ring, HSTR) and 1000 Mb/s (Gigabit Token-Ring). Companies that promote Token-Ring (among them IBM, Olicom, Madge) should not try to think of us as their own, looking at it as a good competitor to Ethernet.
In pairs with Ethernet equipment, Token-Ring equipment is much more expensive, because the folding method of managing the exchange is victorious, and Token-Ring does not have such a wide width.
However, on the Ethernet interface, Token-Ring networks are much more likely to have a high profitability rate (more than 30-40%) and guarantee an hour of access. It is necessary, for example, at the borders of a common confession, in some obscurity, the reaction to the outward weather can lead to serious accidents.
The Token-Ring network uses a classic token access method, so that a token constantly circulates around the ring, so that subscribers can receive their data packets (div. Fig. 4.15). It is important to note the importance of the number of links, as the number of conflicts, but also the shortcomings, the need to control the integrity of the marker and the staleness of the function of the link to the skin subscriber (in case of malfunctions, the subscriber has to be switched on).
Token-Ring packet transmission time limit 10 ms. For the maximum number of subscribers 260, the last cycle of the warehouse operation is 260 x 10 ms = 2.6 s. In one hour, 260 subscribers will be able to transfer their packets (so, obviously, they can transfer). For tsey hour vіlny marker obov'yazkovo didde to the skin subscriber. This interval is the upper time limit for Token-Ring access.
Merezha Arcnet
Merezha Arcnet (or ARCnet in English Attached Resource Computer Net, computer network of resources) is one of the oldest merezh. Vaughn was broken up by the Datapoint Corporation back in 1977. International standards for the measurement of the day, although it is considered to be the ancestor of the method of marker access. Regardless of the current standards, until recently (1980 - 1990) the Arcnet network was popular, and seriously competed with Ethernet. A lot of companies have made equipment for this type of merchandise. But at the same time, the versatility of the Arcnet hardware is practically pinned down.
Among the main advantages of Arcnet and Ethernet pairing are the low access time, the high reliability of the connection, the ease of diagnostics, and the low availability of adapters. To the most small amounts, one can see the low speed of transmission of information (2.5 Mb/s), the addressing system and the format of the packet.
For transmission in Arcnet measure, it is necessary to complete a logical code, for which a logical unit has two pulses over a bit interval, and a logical zero has one pulse. Obviously, this code, which is self-synchronizing, which means more cable bandwidth, lower Manchester.
As the medium of transmission of the wire, a coaxial cable with a flexible support of 93 Ohm is used, for example, brand RG-62A/U. Variants with a twisted pair (screened and non-screened) did not have a wide width. There were proponations and options on fiber optic cable, but the stench also did not turn Arcnet.
Like the topology of the Arcnet network, the classic bus (Arcnet-BUS), as well as the passive star (Arcnet-STAR). Concentrators (habi) are found at the vicory. It is possible to connect for additional concentrators of bus and mirror segments in a tree-like topology (like in Ethernet). The smut is free-flowing - the topology is not guilty of closed paths (zavіs). One more exchange: the number of segments, joined by the last lancet for additional concentrators, is not guilty of revisiting the three.
Also, the topology of the Arcnet network can look like this (Fig. 7.15).

Rice. 7.15. Topology of the Arcnet network to the bus type (B - adapters to work in the bus, S - adapters to work from the outside).
The main technical characteristics of the Arcnet mesh are offensive.
· Transmission medium - coaxial cable, twisted pair.
· The maximum length of the fence is 6 kilometers.
· The maximum cable length from the subscriber to the passive hub is 30 meters.
· The maximum cable length from the subscriber to the active hub is 600 meters.
· The maximum cable length between active and passive hubs is 30 meters.
· The maximum cable length between active hubs is 600 meters.
· The maximum number of subscribers for the Merezha is 255.
· The maximum number of subscribers on the bus segment is 8.
· The minimum distance between subscribers at the bus is 1 meter.
· The maximum length of the tire segment is 300 meters.
· Transmission speed – 2.5 Mb/s.
When folding folding topologies, it is necessary to make sure that the faucet of rozpovsyudzhennya signals at the border between subscribers does not exceed 30 μs. The maximum attenuation of the signal in the cable at a frequency of 5 MHz cannot exceed 11 dB.
In the Arcnet measure, the token access method (method of transfer of rights) is distinguished, but in some cases it is similar in the Token-Ring measure. The closest method to that, which is the transfer of the IEEE 802.4 standard.
So, just like the Token-Ring option, Arcnet conflicts are turned off for the most part. As if it were a marker on a link, Arcnet does a good job of guaranteeing the value of an hour for access to a link (to Ethernet). The last hour of bypassing all subscribers becomes 840 ms as a marker. Obviously, this very interval sets the upper time interval for access to the border.
The marker is formed by a special subscriber - the controller of the measure. It is a subscriber with a minimum (zero) address.
Merezha FDDI
Merezha FDDI (kind of English Fiber Distributed Data Interface, fiber optic branching of the data interface) is one of the latest developments of standards for local networks. The FDDI standard has been approved by the American National Standards Institute ANSI (ANSI specification X3T9.5). We have adopted the ISO 9314 standard, which complies with the ANSI specifications. The riven of standardization of the measure is high.
In view of other standard local networks, the FDDI standard is more focused on high transmission speed (100 Mbit/s) and on the most promising fiber optic cable. Therefore, in this case, the retailers were not surrounded by the framework of the old standards, which focused on low speed and electric cable.
The choice of fiber optics as the medium of transmission, having distinguished such advantages of the new medium, as a high barrier, the maximum secrecy of the transmission of information and excellent galvanic decoupling of subscribers. The high speed of transmission, as in the case of a fiber optic cable, it is much easier to reach, allowing you to make a lot of tasks that are inaccessible to lesser wires, for example, the transmission of images at a real scale for an hour. In addition, the fiber optic cable easily overcomes the problem of data transmission for a few kilometers without retransmission, which allows you to be large beyond the borders of the borders, which can saturate the city of the city and may, with all the transfer of the local borders (the low border). All this indicated the popularity of FDDI, although it is not as widespread as Ethernet and Token-Ring.
The FDDI standard is based on the method of token access, transferred by the international standard IEEE 802.5 (Token-Ring). Bearing authority in accordance with the standard, it is necessary to ensure high security of transmission on a large scale. Topology of FDDI network - ce kіlce, the most appropriate topology for fiber optic cable. The Merezhi has two RIZNEPRAMOVAMOVAMOVOLOKOL CABLILI, one call to the reserve, one of the rifle, the Vicoristovati INFORMASTARI (one -time at the Twes) Mbit/s). Zaryano-Kiltseva topology with concentrators included in the ring (like Token-Ring) is also established.
Main technical characteristics of FDDI.
· The maximum number of subscribers in the merezhі is 1000.
· The maximum length of the fence is 20 kilometers.
· The maximum distance between the subscribers of the merezhі is 2 kilometers.
· The transmission medium is a multimodal fiber optic cable (it is possible to stop the electric torsion of the bet).
· Access method - Marker.
· Transmission speed – 100 Mb/s (200 Mb/s for duplex transmission mode).
The FDDI standard has significant advantages, compared with the previously considered measures. For example, Fast Ethernet merging, which can have the same throughput of 100 Mb/s, cannot be compared with FDDI beyond the allowed merging sizes. Before that, the marker access method FDDI provides for CSMA/CD access guarantees for an hour of access and the same number of conflicts for any level of vanity.
The fencing on the fenced yard of the fence, 20 km away, is connected not with the extinguishing of the signals at the cable, but with the need for the fencing of the hour of the complete passage of the signal along the ring to ensure the maximum allowable access. And the maximum axis between subscribers (2 km with a multimode cable) is due to the fact that the signals at the cable are extinguished (it is not guilty of overshooting 11 dB). It is also possible to install a single-mode cable, and in this case, between subscribers, it can reach 45 km, and the total length of the cycle is 200 km.
It is also the implementation of FDDI on an electric cable (CDDI - Copper Distributed Data Interface or TPDDI - Twisted Pair Distributed Data Interface). With this twist, a cable of category 5 with RJ-45 roses is used. The maximum distance between subscribers in any given day can be no more than 100 meters. Varity of possession of a wire on an electric cable at a small scale. However, this version of the network no longer has such obvious advantages over competitors, like FDDI fiber optics. Electrical versions of FDDI are standardized more expensive than fiber optics, so the totality of the possession of other types is not guaranteed.
For transmission to FDDI, a 4V / 5V code is required, specially decomposed for this standard.
The FDDI standard for achieving high fidelity services for transmission included in the ring of subscribers of two types:
· Subscribers (stations) of class A (subscribers of a mobile connection, DAS - Dual-Attachment Stations) are connected to both (internal and external) networks. In case of realizing the possibility of exchange with a speed of up to 200 Mbit / s, or a backup cable is used (at the same time, a backup cable is used for the main cable). The equipment of this class is located in the critical parts of the fence.
· Subscribers (stations) of class B (single-attachment subscribers, SAS - Single-Attachment Stations) are connected to only one (outer) ring of the network. The stench is simple and cheap, comparable with class A adapters, but you can’t imagine their possibilities. At the edge of the stink, only through the concentrator or bypass switch can be switched on, which mimics them in case of accidents.
In addition, all subscribers (computers, terminals, etc.) have Wiring Concentrators connected to each other, the inclusion of which allows picking up all connection points in one place with the method of monitoring the operation of the network, diagnosing malfunctions and simplifying reconfiguration. In case of congestion of cables of various types (for example, fiber optic cable and torsion of a bet), the concentrator also loses the function of converting electrical signals into optical ones. The concentrators also use a sub-connection (DAC - Dual-Attachment Concentrator) and a single connection (SAC - Single-Attachment Concentrator).
An example of changing the dimensions of FDDI representations in fig. 8.1. The principle of uniting the annex in the merezhі is illustrated in Fig. 8.2.

Rice. 8.1. Butt configuration FDDI.
On the view of the access method, which is proponated by the IEEE 802.5 standard, FDDI will stop the so-called multiple token transfer. If in the case of the Token-Ring merger, a new (valid) token is transmitted by the subscriber only after the return to the new packet, then the FDDI new token is transmitted by the subscriber immediately after the completion of the transfer of the packet to him (similar to how to work with the ETR method in the Token-Ring merge ).
At the end, it should be noted that, regardless of the obvious advantages of FDDI, the measure was not wide-width, which is tied to the top rank with a high variety of її equipment (nearly a few hundreds and a thousand dollars). The main sphere of FDDI contagion at a time is the basic, supporting (Backbone) lines, which should be combined with a sprat. Zastosovuetsya FDDI for zadnannya working stations or servers that require high-speed exchange. It is believed that the Fast Ethernet network can outperform FDDI, fiber optic cable protection, marker management method and record allowable network size to set FDDI ahead of competition. And in case of bets, if the variance of the equipment is less important, it is possible to install the version of FDDI based on bet twists (TPDDI) on non-critical sites. In the meantime, the versatility of FDDI hardware may vary greatly due to the release rate.
Merezha 100VG-AnyLAN
Merezha 100VG-AnyLAN - is one of the remaining retailers of high-width local merezha, which has recently appeared on the market. It is in compliance with the international standard IEEE 802.12, the level of standardization is high.
The main advantages are the high exchange rate, relatively low equipment variability (approximately twice as expensive for the most popular 10BASE-T Ethernet network), the centralization method for managing the exchange without conflicts, as well as the sum of the Token-Ring packets in the Ethernet format.
In the name of the 100VG-AnyLAN measure, the number 100 is based on the speed of 100 Mb/s, the letters VG mean a cheap, non-cracked twisted pair of category 3 (Voice Grade), and AnyLAN (be it a link) means those that are combined with the two largest links.
Main technical characteristics of 100VG-AnyLAN:
· Transmission speed – 100 Mbit/s.
· Topology - a star with the possibility of growing (tree). The number of cascading concentrators (hubs) - up to 5.
· Access method - centralization, conflict-free (Demand Priority).
· Transmission medium – quad unshielded twisted pair (UTP category 3, 4 or 5 cables), double twisted pair (UTP category 5 cable), double shielded twisted pair (STP), as well as fiber optic cable. At the same time zdebіlshgo widened chotirivіrna twisted pair.
· The maximum length of the cable between the concentrator and the subscriber and between the concentrators is 100 meters (for UTP cable of category 3), 200 meters (for UTP cable of category 5 and shielded cable), 2 kilometers (for fiber optic cable). The maximum possible size of the fence is 2 kilometers (subject to allowable hiccups).
· The maximum number of subscribers is 1024, recommended is up to 250.
Thus, the parameters of the 100VG-AnyLAN measure are close to those of Fast Ethernet. However, the main advantage of Fast Ethernet is the totality of the most advanced Ethernet network (in case of 100VG-AnyLAN, which one needs space). At the same time, the centralized management of 100VG-AnyLAN, which includes conflicts and guarantees the time limit for access (which is not transferred to the Ethernet network), also cannot be dropped from the accounts.
The butt structure of the 100VG-AnyLAN measure is shown in fig. 8.8.
The 100VG-AnyLAN network is composed of a central (main, root) concentrator of level 1, which can be connected as a number of subscribers, and concentrators of level 2, which subscribers and concentrators of level 3 can be connected to their own line. In this merezha, the mother may have more than five such equals (in the cob variant, there were more than three). The maximum betting limit can be 1000 meters for non-canceled twisted bets.

Rice. 8.8. The structure of the 100VG-AnyLAN.
For non-intelligent hubs of other networks (for example, Ethernet, Token-Ring, FDDI), 100VG-AnyLAN array hubs are smart controllers that provide access to the array. For whom the stink is constantly controlled and drunk, which is available at all ports. Concentrators accept packets as they come, and forward them only to such subscribers, as they are addressed. However, no stink of information is generated, so it is not active to enter this mode, but it is not a passive star. Hubs cannot be called full subscribers.
The skin from the concentrator can be used with Ethernet packet formats and Token-Ring. With this concentrator, all services are responsible for processing packages with only one format. For communication with Ethernet and Token-Ring networks, you need to do it easily.
Concentrators may have one port of the upper level (for connecting to the concentrator of the higher level) and a few ports of the lower level (for connecting subscribers). As a subscriber, you can act as a computer (working station), server, location, router, switch. Another concentrator can also be connected to the port of the lower river.
The skin port of the hub can be set to one of two possible operating modes:
· Normal mode of transferring to the subscriber, delivered to the port, only packets addressed especially to you.
· Monitor mode transmitting to the subscriber, which arrived to the port, all packets, which should be sent to the concentrator. This mode allows one of the subscribers to control the robot as a whole (to override the monitoring function).
The method for accessing a 100VG-AnyLAN tier is typical for a tier with a mirror topology.
When choosing a quad twisted bet, the transmission over the skin of four twisted pairs is carried out at a rate of 30 Mbps. The total speed of transmission is 120 Mb/s. However, the basic information after using the code 5B/6B is transmitted only with a speed of 100 Mb/s. In this rank, the throughput of the cable can be no less than 15 MHz. We are happy with the cable with twisted pairs of category 3 (smart bandwidth - 16 MHz).
Thus, 100VG-AnyLAN is an affordable solution for increasing transmission speed up to 100 Mb/s. However, there is not a lot of totality with the same standard measures, so farther away the share is problematic. Until then, on the FDDI board, there are no record-breaking parameters. More than anything, 100VG-AnyLAN is not respectful of the support of reputable companies and the high level of standardization will be left with just the butt of cіkavih technical solutions.
Speaking of the widest 100-megabit Fast Ethernet network, 100VG-AnyLAN secures the largest UTP category 5 cable (up to 200 meters), as well as a conflict-free exchange management method.
Significantly, the main features of the development of the Ethernet network and the transition to the Fast Ethernet network (IEEE 802.3u standard):
- - tenfold increase in throughput;
- - Preservation of the CSMA/CD vipad access method;
- - Save frame format;
- - Supporting the traditional media of data transmission.
The designation of power, as well as the support of two speeds and the auto-allocation of 10/100 Mbit / s, which will be in the network of cards and Fast Ethernet switches, allow you to make a smooth transition from the Ethernet network to the larger Fast Ethernet network, preventing the technology from occurring at the time. Another additional factor in successful market penetration is the low availability of Fast Ethernet.
Architecture to the Fast Ethernet standard
The structure of the Fast Ethernet layers (including the MII interface and the Fast Ethernet transceiver) is shown in fig. 13. Even at the stage of development of the 100Base-T standard, the IEEE 802.3u committee determined that there is no universal signal encoding scheme that would be ideal for all three physical interfaces (TX, FX, T4). If compared with the Ethernet standard, then there the coding function (Manchester code) is disabled by the PLS physical signaling level (Fig. 5), which is more known for the middle AUI interface. For the Fast Ethernet standard, the coding function exceeds the PCS coding level, located below the middle MII interface. As a result, the skin transceiver is responsible for choosing its own set of coding schemes that are best suited for a different physical interface, for example, dialing 4V / 5V and NRZI for a 100Base-FX interface.
МII interface and Fast Ethernet transiver. The MII (medium independent interface) interface of the Fast Ethernet standard is analogous to the AUI interface of the Ethernet standard. MII interface secures communication between drivers and physical coding. The main yoga recognition is the simplest selection of various types of the medium. The MII interface is transferred farther away from the connection of the Fast Ethernet transceiver. For connection, a 40-pin socket is used. The maximum distance on the ІІІ interface cable is not liable to exceed 0.5 m.
Although there may be standard physical interfaces (for example, RJ-45), the structure of the physical level drive can be attached to the middle of the microcircuit with great integration of logic. In addition, let's allow the entry in the protocols of the interim transfers in a single annex, which should be used as the main method for the growth of swedcodes.
Physical interfaces Fast Ethernet
The IEEE 802.3u Fast Ethernet standard established three types of physical interface (Fig. 14, Table 6. Main characteristics of physical interfaces in the IEEE 802.3u Fast Ethernet standard): 100Base-FX, 100Base-TX and 100Base-T4.

100Base-FX. The standard for this fiber optic interface is basically identical to the FDDI PMD standard. The main optical standards are 100Base-FX є Duplex SC. The interface allows a duplex channel to communicate.
- * - available only in full duplex mode.
- 100Base-TX. The standard of the physical interface for transmitting non-cabled twist betting is not lower than category 5. It is identical to the FDDI UTP PMD standard. Physical port RJ-45, as standard 10Base-T, can be of two types: MDI (multiple cards, workstations) and MDI-X (Fast Ethernet repeaters, switches). An MDI port is available for a number of Fast Ethernet repeaters.
For transmission by medium cable, bets 1 and 3 are won. Bets 2 and 4 are free. The RJ-45 port on the secondary card on the switch can support either 100Base-TX mode or 10Base-T mode, or the auto-configuration function. Most of the current mesh cards and switches support this function with RJ-45 ports and, for the most part, can work in duplex mode.
100Base-T4. This type of interface allows the provision of a full duplex channel for torsion pair UTP cat. 3 and higher. The very possibility of transitioning from the Ethernet standard to the Fast Ethernet standard without radical replacement of the basic cable system based on UTP cat.3 should be considered the main advantage of this standard.
On the basis of the 100Base-TX standard, only two twisted pairs of the cable are twisted for transmission, in the 100Base-T4 standard all pairs of pairs are twisted. Moreover, when linking a working station, repeating for an additional direct data cable to the working station, before repeating, go along twisted pairs 1, 3 and 4, and at the return line - along pairs 2, 3 and 4, similar to the Ethernet standard. Other two bets 3 and 4 alternately, alternately in teams, can pass the signal either in one or the other directly. Signal transmission in parallel for three twisted pairs is equivalent to inverse multiplexing, considered in section 5. Bit rate for one channel becomes 33.33 Mb/s.
Symbol coding 8V/6T. Yakby won the Manchester coding, then the bit security of the single twisted pair was 33.33 Mbit / s, which exceeded the 30 MHz boundary for such cables. Efficiently changing the modulation frequency is possible, so that the replacement of the direct (two-line) binary code can be changed to a three-way (ternary) code. Tsey code v_domy yak 8V/6T; tse means that the first, lower transmission is used, the skin is set from 8 binary battles (symbol) on the back of the head it is converted in the same way to the first rules of 6 triple (tririval) symbols.
The 100Base-T4 interface may have one shortcoming - the impossibility of supporting the duplex transmission mode is important. And even if there are small Fast Ethernet networks with multiple repeaters 100Base-TX can not overcome 100Base-T4 (with a multi-colour domain, the bandwidth of which is no more than 100 Mbps), then if there is a network with it, there will be an obvious switcher serious. Therefore, this interface does not have such a great extension, like 100Base-TX and 100Base-FX.
Types of Fast Ethernet Attachments
The main categories of attachments that can be used in Fast Ethernet, as well as Ethernet: transivers; converters; Merzhezhі maps (for installation on a work station/file server); repeaters; commutators.
Transiver- a two-port attachment that includes PCS, PMA, PMD and AUTONEG, and may, from one side, МII interface, from the other - one of the middle physical interfaces (100Base-FX, 100Base-TX or 100Base-T4). The transceivers are vicariously sparsely, as well as vicoristic cards, repeaters, commutators with MII interface.
Merezheva map. The largest expansion of today's cards with 100Base-TX interface on the PCI bus. Neobov'yazykovimi, albeit even more important, functions to the RJ-45 port - autoconfiguration 100/10 Mbit / s and support for duplex mode. Most of the current maps support these functions. There are also several cards with 100Base-FX optical interface (IMC, Adaptec, Transition Networks etc.) - the main standard optical SC rosettes (ST is allowed) on the Bagatomodov OB.
Converter(media converter) - a two-port attachment, an insult to what it is to represent an interface of a medium-sized country. Converters, on the vіdminu vіdminu vаchіv, mаy prаsyuvati v duplex krіm vpadku, if є port 100Base-T4. Extended 100Base-TX/100Base-FX converters. Looking at the global trends in the growth of wide-range lingering lines with the help of single-mode fiber optic cables, the shifting of optical receivers to single-mode optical fiber has increased dramatically in the last ten years. The converter chassis, which combines a small number of 100Base-TX / 100Base-FX modules, allows the connection of anonymous fiber-optic segments, which converge in the central hub, to a switch equipped with RJ-45 (100Base-TX) duplex ports.
Repeater According to the parameter of maximum tim-hour blockages during relaying frames, Fast Ethernet repeaters are divided into two classes:
- - Class I. Trimming on the RTD underpass can be over 130 watts. Through a smaller number of vimogi, repeating the same class, mothers can port T4 and TX / FX, as well as be stacked.
- - class II. Prior to the repetition of this class, there are some short cuts on the subway run: RTD
Switch- important attachment of corporate merezh. Most of today's Fast Ethernet switches support auto-configuration of 100/10 Mb/s RJ-45 ports and can provide full-duplex communication on all ports (100Base-T4 with a twist). The switches can have special add-on slots for installing an uplink module. The interfaces of such modules can be optical ports such as Fast Ethernet 100Base-FX, FDDI, ATM (155 Mbit/s), Gigabit Ethernet etc.
Great switches Fast Ethernet companies: 3Com, Bay Networks, Cabletron, DEC, Intel, NBase, Cisco etc.
fast ethernet
Fast Ethernet - specification IEEE 802.3 and officially adopted on 26 June 1995 is the standard for a channel layer protocol for networks operating with both a medium and a fiber optic cable with a speed of 100 Mb / s. New specification to reduce the Ethernet IEEE 802.3 standard, adopting such a frame format, a CSMA/CD media access mechanism and a star topology. The evolution came across a number of elements in the configuration of the physical level, which made it possible to increase the capacity of the building, including the type of cable, the length of the segments and the number of concentrators.
Fast Ethernet structure
In order to better understand the robot and understand the interplay of Fast Ethernet elements, moving up to Figure 1.
Figure 1. Fast Ethernet system
Logic call control (LLC)
The IEEE 802.3 u specification splits the channel layer into two layers: logical link control (LLC) and media access (MAC), which will be discussed below. LLC, the functions of which are designated by the IEEE 802.2 standard, actually provide interoperability with higher-level protocols (for example, with IP or IPX), providing various communication services:
- Service without a confirmation of acceptance. A simple service that does not manage the flow of data or control pardons, and also guarantees the correct delivery of data.
- Service from the installation of the day. Absolutely reliable service, which guarantees the correct delivery of data for the account of the installation from the system-acceptance to the beginning of the transfer of data and the use of mechanisms for the control of pardons and control of the flow of data.
- Service without the confirmation of acceptance. The middle service, a kind of victorious confirmation of acceptance for secure guaranteed delivery, but does not set the date before the transfer of data.
On the transmission system, the data transferred down under the tie line protocol is encapsulated under the LLC line. The standard is called єх Protocol Data Unit (PDU, protocol data unit). If the PDU is passed down under the MAC level, it is again framed by the header and post-information, at this point it can technically be called a frame. For an Ethernet packet, ce means that the 802.3 crim data frame is to contain the three-byte LLC header. Thus, the maximum allowable length of data for a skin package is changed from 1500 to 1497 bytes.
The title LLC consists of three fields:
In some cases, LLC personnel play an insignificant role in the process of exchanging money. For example, in a measure that has a TCP/IP order with other protocols, a single LLC function can affect the ability of 802.3 frames to pass the SNAP header, similar to Ethertype specifying the Merezhevoy Rivne protocol, which is responsible for either frame transmissions. For this reason, all PDU LLCs have an unnumbered informational format. Prote іnshі vysokor_vnevі protocols vіmagayut vіd LLC extended servіsu. For example, the NetBIOS sessions and the number of NetWare protocols override the LLC services from the installed sites.
SNAP header
The receiving system must be determined which of the protocols in the measure is responsible for taking the input data. For 802.3 packets, within the LLC PDU, one more protocol is zastosovuetsya, titles sub-networkAccessprotocol(SNAP, protocol for access to pіdmerezh).
The SNAP header can be up to 5 bytes long and is populated without intermediary after the LLC header data field in the 802.3 frame, as shown in the thumbnail. The header contains two fields.
Organization code. Organization Identifier or Browser - This is a 3-byte field that has the same value as the first 3 bytes of the MAC address of the directory in the 802.3 header.
local code. Local Code - This field is up to 2 bytes long and is functionally equivalent to the Ethertype field in the Ethernet II header.
Good weather
As it was said earlier, Fast Ethernet has evolved the standard. MAC allocation to the AUI interface, it is necessary to convert for the MII interface, which is supported in Fast Ethernet, for which purpose it is necessary.
Media Access Control (MAC)
Skin vuzol at the edge Fast Ethernet can access controller to the medium (MediaAccessController- MAC). MAC may be a key value for Fast Ethernet and may have three features:
The most important of the three is the MAC first. For whether it's a lace technology, like a vicorist's hearty middle, the rules for access to the middle, which is to be determined, if the vuzol can be transmitted, it's the main characteristic. Rozrobkoy access rules to the middle are engaged in a few committees of ІEEE. The 802.3 committee, which is often called the Ethernet committee, defines the standards for LOM, in which the rules under the name CSMA/CD(Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection - multiple access from carrier control and conflict detection).
CSMS/CD - media access rules for either Ethernet or Fast Ethernet. By itself, in this gallery, two technologies are being used again.
Oskelki all the universities in Fast Ethernet copiously beat the very middle, they can only transmit the stink only once, if it’s necessary. Viznachayut qiu cherga rules CSMA / CD.
CSMA/CD
MAC Fast Ethernet controller, first lower transmission, eavesdropping. Carrying more than once, if another university was transmitting. The PHY value determines the presence of the carrier and generates alerts for the MAC. It’s easy to talk about those who occupy the middle and the hearing vuzol (or vuzli) is guilty of giving up the transmitting one.
MAC, which may be the frame of transmission, the first time to transmit it, is to blame for the slightest delay in the hour after the end of the forward frame. This hour is called interpacket gap(IPG, interpacket gap) and three times 0.96 microseconds, that is the tenth part of an hour of transmission to a packet of 10 Mbit / s extraordinary Ethernet packet (IPG is a single interval of an hour, it is always measured in microseconds, but not in a bit hour) Figure 2.

Malyunok 2. Inter-packet gap
After the completion of the package 1, all the universities of the LOM dues will receive an IPG for an hour, the first time can be transmitted. Time interval between packets 1 and 2, 2 and 3 in Fig. 2 - 1 hour IPG. After the completion of the transfer of package 3, it is time for the availability of material for processing, so the hourly interval between packages 3 and 4 is lower, lower IPG.
All universities are responsible for complying with these rules. If you have to send a lot of frames for transmission and data to the university as the only transmitting one, then after the overstretching of the skin package of wines, it is to blame for the transfer of the IPG hour.
For the most part, CSMA rules access to Fast Ethernet. Shorter seeming, richly vuzlіv mayut access to the middle and vikoristovuyut carry for the control of yoga occupancy.
In the early experimental meshes, these rules were fixed, and such meshes worked even better. The CSMA litigation has brought the issue to a close. Often two Woozleys, making a packet for transmission, and after waiting an hour for IPG, began to transmit at the same time, which led to the creation of data on both sides. Such a situation is called collation(collision) chi conflict.
For podlannya tsієї pereshkodi early protocols began to complete a simple mechanism. The packets were divided into two categories: commands and reactions. The skin command, as it was transmitted by the node, signaled the reaction. As long as the last hour (called the timeout period) after the command was sent, the reaction to it was not taken away, then the command was issued again. Tse could vydbuvatisya kіlka razіv (border kіlkіst time-outs), the first lower transmission vuzol fixing a pardon.
Tsya scheme could miraculously work, but only to the singing moment. Viniknennya conflicts led to a sharp decrease in productivity (sounded in bytes for a second), the shards of the university often stood in the cleared commands, which in no way reach the point of recognition. The revantation of the measure, the increase in the number of nodes, without intermediation, caused the increase in the number of conflicts and, also, the decrease in the productivity of the measure.
The designers of the early projects knew the culprit of the problem: the skin vuzol is responsible for establishing the fact that the transmitted package was spent in a way that revealed a conflict (and not to blame for the reaction, which is by no means the case). This means that the communication with the conflict packets may be negligently transferred again until the timeout ends. Likewise, the sender transmitted the remaining bit of the packet without a conflict, and the transmission packet was successful.
The method of controlling the load is good to combine with the function of detecting collisions. Kolіzії still continue to work, but on the productivity of the border they do not see, so that the knots are easily spared. The DIX group, having developed the rules for accessing the CSMA / CD media for Ethernet, designed them as a simple algorithm - Figure 3.

Figure 3. CSMA/CD Robotic Algorithm
Attachment of Physical Equity (PHY)
Fast Ethernet oscillators can use a different type of cable, for the skin environment you need a unique forward signal conversion. The transformation is also necessary for efficient transmission of data: to make transmissions of the code stable until the transfer of codes, it is possible to spend or to create four elements (body), to ensure efficient synchronization of clock generators on the transmitting or receiving side.
Drive coding (PCS)
Encode/decode data that needs to match/match the MAC with different algorithms or .
Pіdrіvnі і physical priєdnannya i zadezhnostі vіd іn physical medium (PMA аnd PMD)
Pіdrіvnі РМА and PMD zdіysnyuyut zv'yazok mіzh pіdrіvnem PSC і MDI interface, zabezpechuyuchi molding vіdpovіdno to the method of physical coding: or .
Automatic call forwarding (AUTONEG)
Auto-negotiation enable allows two ports that interact to automatically select the most efficient operating mode: duplex or duplex 10 or 100 Mbps. Physical Riven
The Fast Ethernet standard defines three types of Ethernet signal transmission media with a speed of 100 Mbps.
- 100Base-TX - two twisted pairs of wires. The transmission is up to the data transmission standard for a twisted physical medium, rozroblenny ANSI (American National Standards Institute - American National Standards Institute). The torsion transmission cable may or may not be screened. Vikoristovu 4V/5V data coding algorithm and MLT-3 physical coding method.
- 100Base-FX - two cores, fiber optic cable. The transmission is also up to the data transmission standard of the fiber optic medium, as decoded by ANSI. Vikoristovu 4V/5V data coding algorithm and NRZI physical coding method.
Specifications 100Base-TX and 100Base-FX also 100Base-X
- 100Base-T4 is a special specification, broken down by the IEEE 802.3u committee. Depending on the specification, data transmission is based on twisted-pair telephone cable, which is called a Category 3 UTP cable. The 8V/6T data encoding algorithm is based on the NRZI physical encoding method.
The Fast Ethernet addendum includes a recommendation to use Category 1 shielded twisted pair cable, which is the standard cable that is traditionally used in Token Ring networks. The support organization and recommendations for using STP cable in the Fast Ethernet network provide a way to transition to Fast Ethernet for customers, as if STP cable distribution is possible.
The Fast Ethernet specification includes an auto-switching mechanism that allows the node port to automatically adjust to the speed of data transmission - 10 or 100 Mb/s. This mechanism is based on the exchange of packets nearby from the port of the concentrator or the relay.
Medium 100Base-TX
As a medium of 100Base-TX transmission, two pairs of bets are made, and one pair is victorious for data transmission, and the other for the receiver. Since the ANSI TP specification - PMD contains descriptions of both shielded and non-shielded twisted pairs, the 100Base-TX specification includes a subset of both non-shielded and shielded twisted pairs type 1 and 7.
MDI (Medium Dependent Interface) socket
The interface to the 100Base-TX channel, which can be found in the medium, can be one of two types. For cable on non-screened twisted pairs like MDI roses, an eight-pin RJ 45 rose of category 5 should be used. For MDI roses, it is necessary to select the IBM type 1 STP roses, which are screened with DB9 roses. Such roses sound like zastosovuetsya at Token Ring chains.
Category 5(e) UTP cable
In the interface of the UTP 100Base-TX medium, two pairs of wires are twisted. For minimization of cross-pointing and possible creation of a signal, chotiri droti is not guilty of vikoristovuvatisya with the method of transmission of any signals. Signals for transmitting and receiving skin steam are polarized, with one wire transmitting a positive (+) signal and the other a negative (-) signal. The color marking of wires in the cable and the numbers of contacts in the rose for 100Base-TX wires are indicated in Table. 1. Although the PHY 100Base-TX branch was expanded after adopting the ANSI TP-PMD standard, however, the pin numbers on the RJ 45 socket have been changed to accommodate the wiring scheme that is already adopted in the 10Base-T standard. In the ANSI TP-PMD standard, pins 7 and 9 are set to receive data, while in the 100Base-TX and 10Base-T standards for which pins 3 and 6 are recognized. T and їх connection to quiet category 5 cables without changing the wiring. For RJ 45 roses, pairs of wires that are twisted are connected to contacts 1, 2 and 3, 6. For the correct connection of wires, the following color markings are wired.
Table 1. Socket contact assignmentsMDIcableUTP100Base-TX
Vuzli vzaєmodіyut mіzh a way to exchange frames (frames). In Fast Ethernet, a frame is the basic unit of exchange of information - be it information that is transmitted between nodes, to be located in the field of data of one number of frames. The transfer of personnel from one node to another is only possible for the obviousness of the method of unambiguous identification of all nodes in the network. That's why the skin is wuzol at the LOM address, as it is called the MAC address. This address is unique: the same two nodes of the local network cannot have the same MAC address. What's more, in the same time with the LOM technology (behind the ARCNet vinnyatka) the same two nodes in the world cannot have the same MAC address. Whether it be a frame to take revenge, take three main portions of information: the address of the owner, the address of the owner and the data. Deyakі cadres wash other fields, ale obov'yazykovymi є less than three lists. On little 4, the structure of the Fast Ethernet frame is shown.
4. frame structureFastethernet
- owner addresses- Specify the addresses of the node that will take the data;
- addresses of the manager- Specify the addresses of the node that sent data;
- Dozhina/Type(L/T - Length/Type) - information about the type of transferred data is sent;
- checksum frame(PCS - Frame Check Sequence) - recognized for checking the correctness of the frame received by the receiving node.
The minimum limit for a frame is 64 octets, or 512 bits (terms octetі byte - synonyms). The maximum limit for a frame is 1518 octets, or 12144 bits.
Frame addressing
A node on a Fast Ethernet network has a unique number, which is called the MAC address or node address. This number is accumulated from 48 bits (6 bytes), assigned to the interfacing interface for an hour of preparation, I will attach it and program it at the initialization process. To that end, the interface of all LOM, with ARCNet's blame, as a vicorous 8-bit address, which is assigned by the administrator, may be assigned a unique MAC address, which will be determined by the MAC address on Earth and assigned by the IEEE weather forecaster.
To make it easier to manage media interfaces, the IEEE has proposed dividing the 48-bit address field into several parts, as shown in figure 5. The first two bits of the address (bits 0 and 1) are proportional to the address type. The value of the paraportions depends on the method of interpreting the address part (bits 2 - 47).

Baby 5. MAC address format
The I/G bit is called ensign of an individual/group address and show which (individual or group) addresses. Individual addresses are given to only one interface (or node) in a merezh. Addresses for which I/G bits have 0 - ce MAC addresses or node addresses. If the I/O bit is set to 1, then the addresses are added to the group and called rich-point address(multicast address) or functional address(Functional address). Group addresses can be assigned to one or more sub-interfaces of LOM. Frames, sent for a group address, remove or copy all the interfaces of the SCRAP that you can use it. Bagatopoint addresses allow you to send a frame to anonymous nodes in a local network. If the I/O bit is set to 1, then bits from 46 to 0 are treated as a richpoint address, and not as the U/L, OUI, and OUA fields of the original address. Bit U/L is called Ensign of the Universal/Mistic Administration and determines how the address was assigned to the media interface. If the bits, I/O and U/L, are set to 0, then the addresses are given by a unique 48-bit identifier, described earlier.
OUI (organizationally unique identifier - organizational-unique identifier). IEEE provides one or more OUIs to the skin maker of interfacing adapters and interfaces. The skin picker is confirmed for the correct assignment of the OUA (organizationally unique address - organizationally unique addresses), which is guilty of the mother, be it the creations of his attachments.
When setting the U/L bit of the address, it is locally kerned. Tse means that the wine is not a common interface. Whether or not an organization can create its own MAC address of the media interface by setting the U/L bit to 1, and bits from the 2nd to the 47th in the same value. Merezhevy interface, after retrieving the frame, forward the decoder to the address of the owner. When installed on the address of the I / O bit, the MAC level removes the entire frame less often, as the address is changed from the list, which is taken to the node. This technique allows one node to send a frame to multiple nodes.
Іsnuє special bagatopoint address, rank wide address. A 48-bit wide IEEE address has all bits set to 1. If a frame is transmitted with a host wide address, all nodes in the border are discarded and processed.
Dovzhin Field/Type
The L/T (Length/Type) field is reserved for two different purposes:
- the designation of the data fields of the frame, including whether it is supplemented by gaps;
- for understanding the type of data in poly data.
The value of the L/T field, which is in the interval between 0 and 1500, is the length of the data field of the frame; The next value indicates the protocol type.
The field of L/T was a historical siege of the standardization of Ethernet in the IEEE, which gave rise to a number of problems from the totality of the possession, released before 1983. In the meantime, Ethernet and Fast Ethernet are by no means victorious in the field of L/T. The field is assigned to serve no longer for the benefit of software security, processing frames (that is, by protocols). Besides, the only standard definition of the L/T field is that it can be used as a data type field. The standard is to say: "Frames with the values of the field, which are changed in paragraph 4.4.2, can be ignored, discarded, or rewritten. The selection of these frames should go beyond the international standard."
As I said, respectfully, the L/T field is the primary mechanism frame type. Fast Ethernet and Ethernet frames, for which values of the L/T field are set to a value (L/T 802.3 values, frames, for which field values are set to data type (L/T value > 1500), are called frames ethernet- II or DIX.
field of tribute
At the field of data information is to be cleared, as if one vuzol was sent to another. On the vіdmіnu vіd іnshih polіv, scho save even speсificі vіdomosti, the data field can vengeance may be the same information, abi її obsyag becoming less than 46 and three more than 1500 bytes. How it is formatted and interpreted in place of the data fields, define protocols.
If it is necessary to send data less than 46 bytes, LLC will add up to the end of bytes with unknown values, titles insignificant tributes(Pad data). As a result, the field length is 46 bytes.
If the frame is type 802.3, then the L/T field must be specified with the value of the actual data. For example, if a 12-byte message is sent, then the L/T field takes the value 12, and the data field takes 34 additional minor bytes. Adding insignificant bytes is initiated by LLC Fast Ethernet and sound is implemented by the hardware.
Please do not set the L/T fields instead - for security reasons. Setting the value of this field may need to be set by the driver of the merging interface.
Frame Checksum
The frame check sum (PCS - Frame Check Sequence) allows you to reconsider, so that the frames are not deleted. When forming a frame that is being transmitted, a special mathematical formula is won on the MAC level CRC(Cyclic Redundancy Check - cyclic redundancy code), recognized for calculating a 32-bit value. Remove the value from the FCS field of the frame. At the input of the MAC equal element, calculating the CRC, the values of all bytes in the frame are supplied. The FCS field is the primary and most important mechanism for inducing and correcting pardons in Fast Ethernet. Starting from the first byte of the address, it is completed with the remaining byte of the data field.
Field values DSAP and SSAP
DSAP/SSAP values | Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Indiv LLC Sublayer Mgt |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Group LLC Sublayer Mgt |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SNA Path Control |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reserved (DODIP) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ISO CLNS IS 8473 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 8B6T encoding algorithm converts an eight-bit data octet (8B) into a six-bit ternary character (6T). Code groups 6T are recognized as transmissions in parallel over three twisted pairs of cable, so the effective speed of transmission from skin twisted pairs is one third of 100 Mb / s, tobto 33.33 Mb / s. The speed of transmission of ternary symbols from the skin twists of the pair becomes 6/8 to 33.3 Mbit/s, which operates at a clock frequency of 25 MHz. With such a frequency, the timer is used for the MP interface. At the same time, binary signals, like two equals, ternary signals that are transmitted over a skin pair, can mother three equals.
Character encoding table
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Objectives of work
The metadata of this work is the development of the principles of Ethernet and Fast Ethernet technologies and the practical mastering of methods for assessing the efficiency of a measure, based on Fast Ethernet technology.
Theoretical performance
Ethernet technology. The specification for the Ethernet network was promulgated by DEC, Intel and Xerox (DIX) in 1980, and three years later, based on the standard IEEE 802.3.
The first versions of Ethernet vl.O and Ethernet v2.0, as the transmission medium, only coaxial cable was used. The IEEE 802.3 standard allows twisted-pair and optical fiber as the transmission medium. In 1995 adopted the IEEE 802.3u (Fast Ethernet) standard with a speed of 100 Mbit / s, and in 1997. - IEEE 802.3z (Gigabit Ether 1000 Mb/s). At Vosenya 1999 Adopted standard IEEE 802.3ab - Gigabit Ethernet torsion-free U pair category 5.
In terms of Ethernet (10BASE2, 100BASE-TX and in), the first element indicates the rate of data transmission in Mbit/s; the other element BASE means that it is a direct (non-modulated) transmission; the third element indicates the rounded value of the length of the cable in hundreds of meters (10BASE2 - 185 m, 10BASE5 - 500 m) or the type of transmission medium (T, TX, T2, B T4 - twisted pair; FX, FL, FB, SX і LX - optical fiber; СХ - twinax cable for Gigabit Ethernet).
Ethernet is based on method of multiple access to the transmission medium for interception of the carrier and the detection of collisions - CSMA / CD
- (Carrier Sense with Multiple Access and Collision Detection);
- all adapters can be used for access to the medium (MAU) - a transiver, connections to the central (split) data transmission medium;
- the node's skin adapter before transmitting the information to the line of the signal (carrying);
- then the adapter forms a frame (frame) that starts from the synchronizing preamble, following the flow of two data in the self-synchronizing (Manchester) code;
- other nodes receive messages signal, synchronize on the preamble and decode it into a sequence of bits;
- the end of the transmission of the frame is determined by the reception of the frame in the daytime of the carrier;
- different manifestations collisions(zіtknennya two signals in the form of different nodes) transmitting nodes attach the transmission to the frame, after which, after an interval of one hour (skin through its own), they retry the transmission after the ringing of the line; in case of a black failure, the attempt is made to try (and so up to 16 times), moreover, the interval of the trimming is increased;
- the collision is accepted by a non-standard default frame, as it may be less than 64 bytes, or a preamble;
- between frames is to blame for the safety of the time gap ( interpersonal or interpacket interim, IPG - inter-packet gap) trivality 9.6 µs - the station does not have the right to start transmission earlier, lower through the IPG interval, after the specified moment of loss of the carrier.
Appointment 1. Domain kolіzіy- a group of knots, tied with a glowing core (cables and repeaters) of the transmission.
The length of the domain of colisms is intermingled with an hour of signal extension between the largest distances, one and the same nodes.
Appointment 2. Diameter of the domain of colisms- stand between the two largest in the distance, one in the same end with outbuildings.
Appointment 3. Beat interval- hour, it is necessary to transfer one bit.
The Ethernet bit interval (with a speed of 10 Mb/s) is set to 0.1 µs.
Technology "Fast Ethernet". For Fast Ethernet technology, the value of the bit interval is set to 0.01 µs, which gives a tenfold increase in transmission speed. With this frame format, the total amount of data carried by the frame and the mechanism for accessing the data transmission channel were lost without change in the Ethernet connection.
Fast Ethernet is the medium for data transmission for robots at a speed of 100 Mb/s, as in the IEEE 802.3u specification, it can be designated “100BASE-T4” and “100BASE-TX” (twisted pair); "100BASE-FX" and "100BASE-SX" (fiber).
Rules for budding merezhі
The first model of the network is Fast Ethernet. Model є, vlasne, typing rules and measures (Table L.1):
- - The length of the skin segment of the bet is less than 100 m;
- - The length of the skin fiber optic segment is less than 412 m;
- - if the MP cables (Media Independent Interface) are twisted, then the leather from them can be less than 0.5 m;
- - stubs, which are brought in by the MP cable, are not protected by estimating the time parameters in the line, as stench is a warehouse stub, which is brought in by terminal outbuildings (terminals) and repeaters.
Table L. 1
Maximum allowable diameter for a collision domain in Fast Ethernet
The standard defines two classes of repeaters:
- class I repeaters recode the input signals from the digital view, and when transmitting, recode the digital data from the physical signals; the transformation of signals at the repeater for a certain hour, only one repeater of class I is allowed in the domain of collisions;
- repeaters of class II negligently transmit otrimani signals without any transformation, to which only segments can be connected to them, which have the same ways of encoding data; you can win no more than two repetitions of class II in one domain of colonies.
Another mesh model is Fast Ethernet. Another model is to avenge the sequence of timing changes in time parameters in the measure for the duplex mode of data exchange. The diameter of the domain of colisms and the number of segments in the new circle of subway turnover, which is necessary for the correct operation of the mechanism for detecting and resolving colisms (Table L.2).
Table L2
Timing blockage of components in the Fast Ethernet network
The hour of the subway turnover is secured for the largest (at the sensi rai-space signal) path between two nodes of the kolіzіy domain. Rozrahunok vykonuetsya path pіdsumovuvannya timchasovy zatrimok at the segments, repeating and terminals.
To calculate the hour of the dependent turnover, it is necessary to multiply the value of the segment's average hour of the dependent turnover of the segment. Having designated the hours of the under-rolling turnover for all segments of the largest route, it is necessary to add a trim to them, which should be brought in by a pair of terminal knots and repeaters. For the appearance of non-transferring zatrimok to the final result, it is recommended to add 4 bit intervals (bі) and equalize the result with the number 512. If the result is not exceeded by 512 bі, then the measure is considered to be practical.
Butt of rozrahunku configuration merezhi Fast Ethernet. On fig. L.28 the butt of one of the limitingly permissible configurations of the Fast Ethernet network was introduced.
Rice. L.28. Example of valid Fast Ethernet configuration
The diameter of the domain of the colonies is calculated as the sum of the lengths of the segments A (100 m), B (5 m) and C (100 m) and 205 m. kolіzіy not perevischuє admissible for tsієї konfіguratsії boundary. The commutator (switching hub), which enters the warehouse of the fence (div. Fig. L.28), is taken in by the end of the building, so that the colonies do not expand through it. That 2-kilometer segment of fiber optic cable that goes into the whole switch with a router is not covered by the distribution of the diameter to the domain of the Fast Ethernet network. Merezha follows the rules of the first model.
Let's change it now for another model. The biggest routes in the domain of collisions: from DTE1 to DTE2 and from DTE1 to the switch (switching hub). Offset paths are made up of three segments on twisting pairs, connected by two repeaters of class II. Two segments may have a maximum permissible length of 100 m. The length of the segment, which is repeated, is 5 m.
Assume that all three segments are 100BASE-TX segments and a pair of category 5 is twisted in them. L.Z estimating the value of the hour of the turnaround for the sighted paths (div. Fig. L.28). Having added the numbers from another table in the table, we will take 511.96 bі - tse will be an hour of free turnover for the largest route.
Table L.3
Hour of the turn of the line fast ethernet
It should be noted that in this season there is no insurance reserve of 4 bі, to that in which case there are the most significant losses (Div. Table L.2). The actual clock characteristics of the FastВ Ethernet components can be improved even further.
Head of the Viconan
It is necessary to evaluate the practicality of a 100-megabit Fast Ethernet network comparable to the first and other models. Configuration measures are in the table. L.4. The topology of the mesh is shown in fig. L.29-L.ZO.
Table L.4
Job options
|
Segment 1 |
Segment 2 |
Segment 3 |
Segment 4 |
Segment 5 |
Segment 6 |
|
|
100BASEX, 100m |
100BASETX, 95 m |
100BASETX, 80m |
100BASEX, 100m |
100BASEX, 100m |
|
Segment 1 |
Segment 2 |
Segment 3 |
Segment 4 |
Segment 5 |
Segment 6 |
|
|
YUOWABE-TH, 15 m |
YUOWABE-TH, 5 m |
YuOVAE-TX, 5 m |
100V ABE-EX, 400 m |
YUOWABE-TH, 10 m |
YUOWABE-TH, 4 m |
|
|
YUOWABE-TH, 60 m |
YUOWABE-TH, 95 m |
YUOWABE-TH, 10 m |
YUOWABE-TH, 10 m |
YUOWABE-TH, 90 m |
YUOWABE-TH, 95 m |

Rice. L.29. Topology of mesh 1

Rice. L.30. Topology of mesh 2
Ethernet, all the way down to other less popular devices.Ethernet and Fast Ethernet adapters
Adapter characteristics
Merezhevі adapters (NIC, Network Interface Card) Ethernet and Fast Ethernet can be connected to a computer through one of the standard interfaces:
- ISA bus (Industry Standard Architecture);
- PCI bus (Peripheral Component Interconnect);
- bus PC Card (Won PCMCIA);
Adapters, rozrakhovanі on the system bus (trunk) ISA, until recently, were the main type of adapters. The number of companies that produced such adapters was large, and the same type of attachment was found to be the cheapest. Adapters for ISA are available in 8 and 16 bits. 8-bit adapters are cheaper, and 16-bit adapters are smarter. True, the exchange of information on the ISA bus cannot be too fast (for the inter - 16 MB / s, in reality - no more than 8 MB / s, and for 8-bit adapters - up to 2 MB / s). To that adapters Fast Ethernet, Yaki Vimagayut of Estient Roboti of the Great Shvidoks Priv, and the system of systems of the Shini is not enough to vine. The ISA bus enters the past.
The PCI bus at once practically replaced the ISA bus and became the main expansion bus for computers. It will ensure the exchange of 32-bit data and 64-bit data and will have a high throughput capacity (theoretically up to 264 MB / s), which is quite satisfied with not only Fast Ethernet, but also with Gigabit Ethernet. It is important that the PCI bus is not only installed on IBM PC computers, but also on PowerMac computers. In addition, it supports Plug-and-Play auto-configuration. Maybe, the nearest future one will be more oriented to the PCI bus lace adapters. The lack of PCI in pairing with the ISA bus is that the number of expansion slots in a computer is usually small (say 3 slots). Ale same mesh adapters connect to PCI directly.
The PC Card bus (old name PCMCIA) is currently only found in Notebook-class portable computers. On these computers, the internal PCI bus name should not be displayed. The PC Card interface transfers a simple connection to the computer of miniature expansion boards, and the speed of exchange between these boards is high. Prote more and more portable computers are equipped with tie adapters, oskіlki mozhlivіst access to the merezhі becomes an invisible part of the standard set of functions. New adapters are connected to the computer's internal PCI bus.
When choosing twill adapter, oriented to that other bus, it is necessary, first of all, to switch over, what are the slots for expanding this bus in the computer, what to enter to the border. The next step is to evaluate the laboriousness of installing the adapter and the prospects for the release of boards of this type. The rest may be needed at the time of the exit from the fret.
Zreshtoy, zustrichayutsya mesh adapters, which are connected to the computer through the parallel (printer) LPT port. The main advantage of such an approach is that, with the connection of adapters, it is not necessary to open the computer case. In addition, in this case, the adapters do not occupy the system resources of the computer, such as the channels of the RAP, as well as the addresses of the memory and input/output devices. However, the speed of exchange of information between them and the computer in this way is significantly lower, lower with a different system bus. Until then, the stench takes more than a processor hour to exchange from a network, supporting the computer's robot.
In the rest of the hour, more and more computers are chattering, in which mesh adapters vbudovani at the system board. The benefits of such an approach are obvious: the coristuvach is not guilty of buying the adapter of the thread and installing it in the computer. It is enough to just connect the cable to the outer socket of the computer. However, it is not enough to say that a short-ranger cannot choose an adapter with the best characteristics.
To the other most important characteristics lace adapters you can see:
- adapter configuration method;
- expansion of the buffer memory installed on the board and the modes of exchange with it;
- the possibility of installing a permanent memory chip on the board for remote advancement (BootROM).
- the possibility of connecting the adapter to different types of transmission medium (twisted pair, thin and thin coaxial cable, fiber optic cable);
- vykoristovuєtsya adapter transfer speed through the mesh and the presence of the function її bridging;
- possibility of blocking by the adapter in full-duplex exchange mode;
- the sum of the adapter (more precisely, the driver of the adapter) with the help of the software tools.
The configuration of the adapter was too short for the adapters that were assigned to the ISA bus. The configuration of the transfer is set on the choice of system resources of the computer (addresses for input / output, channels for interrupting direct access to memory, buffer memory address and remote access). Configuring can be done with a path installed in the required position of jumpers (jumpers), or for the help of DOS-configuration programs ( Jumperless , Software configuration), which are added to the adapter. Before the launch of such a program, the program prompts you to install the configuration of the equipment for the help of a simple menu: select the adapter parameters. This program allows you to rob self-test adapter. The selected parameters are stored in the independent memory of the adapter. In any case, when choosing parameters, it is necessary to unify conflicts with system outbuildings computer and with other expansion boards.
The adapter's configuration can be configured automatically in Plug-and-Play mode if computer recovery is enabled. Modern adapters sound to support this mode, so you can easily install a koristuvach.
For the simplest adapters, the exchange from the internal buffer memory of the adapter (Adapter RAM) is carried out through the address space of the input/output device. It is not necessary for this person to configure memory addresses. The base address of the buffer memory used in memory mode must be specified. Vin is assigned to the top memory of the computer (