The maximum frequency of DDR2 RAM. Characteristics and marking of operational memory. Configuration of test benches and software
The German company Qimonda is one of the largest pickers of chips in memory, may today, perhaps, itself wide line any type of product, including memory for mobile devices, and the whole range operational memory for computers, that video memory. Stop, until the speech, - right up to GDDR5, and in the official list there are already two models of such chips - 512 and 1024 megabits, and in the column of readiness before delivery, it’s more typical hour vikoristovuyutsya such chips.
Prote final products, as if it were zatsіkaviti like galuzevyh spozhivachіv, and wide corystuvalny masses, є chips of memory, and modules, the process of preparing them is more simple from a technical point of view, but, more importantly, allow for your own features. For the same reason, under the brand name of chiropractors (there is one thing worth not only Qimonda, but also Samsung, and Hynix), as a rule, they are sold only for non-violent sounds of virobi, building performance at regular frequencies, moreover, it is stable and reliable, but still, it is of interest to the surroundings as an object of follow-up. We, however, failed to learn about such a pair of Qimonda modules with a total volume of 8 GB, and, well, I understand: the scale is very much on the scale of the characteristics of the increase in the size of the microcircuits in the united from the two-banking organization of the module.
Reflect on the topic: what is the need for a commissary, and now such a great memory obyag, within the framework of this article we will not be. Ale, even if you don’t hang around with professional drinks, for which you may need more and more, but you can be surrounded by hostility. simple koristuvach”, which is not to be called by the results of the tests, but rather by the best opinions. Then in such a mood, once thrown into the eyes of the authorities, in pairs with a 4-gigabyte volume, an hour of switching between add-ons, which is signifi- cantly fast. For example, it takes only a few seconds to switch from a daily game to an Internet browser for dozens of seconds. The price, as a minimum, is acceptable, but it’s necessary, and how much you need to pay for it (the modules themselves are more expensive, may have lower high characteristics in the expansion, it’s equal to the extended modules of a smaller volume, so you need to install a 64-bit OS) - virishuvati koristuvachevi. Information about the module builder
Module maker: Qimonda AG
Qimonda AG Module Chip Builder
Module builder website: Starry look module
Module Part Number

Help for decrypting the Part Number of memory modules on the site, also more modules have been re-arranged, which are currently available, and a description of the characteristics. However, the list of such modules, which were found in our order, did not appear (also 4 GB for additional ECC, although our modules do not correct pardons).
Modules with a volume of 4 GB are based on 16 microcircuits BGA-packages in 512M x 64 configuration. The bin guarantees stable operation of modules in DDR2-800 mode at timings of 5-5-5 (RAS value in the description is not guessed, but according to SPD one is 18) life-giving voltage 1.8 V, this mode is used in the SPD microcircuit as a standard mode. The modules are sold in OEM-options, delivered, optionally, in the same way, and combined with a 2-channel kit, the manufacturer does not propagate. SPD chip data
Description to SPD standard:
Description of the standard-specific SPD for DDR2:
| Parameter | Byte | Value | Decryption |
| Fundamental type of memory | 2 | 08h | DDR2 SDRAM |
| Number of address lines of the module | 3 | 0Fh | 15 (RA0-RA14) |
| Total number of address lines of the module | 4 | 0 Ah | 10 (CA0-CA9) |
| Total number of physical banks of the memory module | 5 | 61h | 2 physical banks |
| Memory module data bus call | 6 | 40h | 64 bit |
| Riven life pressure | 8 | 05h | SSTL 1.8V |
| Minimum trivality to the period of the clock signal (t CK) for the maximum stuttering CAS# (CL X) | 9 | 25h | 2.50 ns (400 MHz) |
| Module configuration type | 11 | 00h | Non-ECC |
| Type and method of data regeneration | 12 | 82h | Obviously, "little on the horizon" 82h, which shows a value of 7.8125 ms - 0.5x short self-regeneration |
| Width of the data bus interface (organization type) of the memory chips that are used | 13 | 08h | x8 |
| Width of data bus external interface (organization type) of ECC module memory chips | 14 | 00h | Not appointed |
| Trivality of packets that are transferred (BL) | 16 | 0Ch | BL = 4.8 |
| The number of logical banks in the skin microcircuit of the module | 17 | 08h | 8 |
| Trivality of trimming CAS# (CL), which is supported. | 18 | 70h | CL = 6, 5, 4 |
| Minimum trivality to the period of the clock signal (tCK) with a change in the CAS# trim (CL X-1) | 23 | 25h | 2.5 ns (400 MHz) |
| Minimum trivality to the period of the clock signal (tCK) with a change in the CAS# trim (CL X-2) | 25 | 3Dh | 3.75 ns (266.7 MHz) |
| Minimum hour of recharging data in a row (t RP) | 27 | 32h | 12.5 ns 5,CL=6 5,CL=5 3.33, CL=4 |
| Minimum fading between the activation of the shore rows (t RRD) | 28 | 1Eh | 7.5 ns 3,CL=6 3,CL=5 2CL=4 |
| Minimum fade between RAS# and CAS# (t RCD) | 29 | 32h | 12.5 ns 5,CL=6 5,CL=5 3.33, CL=4 |
| Minimum trivality of the RAS signal pulse # (t RAS) | 30 | 2Dh | 45.0 ns 18,CL=6 18,CL=5 12,CL=4 |
| Capacity of one physical bank of the memory module | 31 | 02h | 2048 MB |
| Renewal period after entry (t WR) | 36 | 3ch | 15.0 ns 6,CL=6 6,CL=5 4,CL=4 |
| Internal shutdown between WRITE and READ (t WTR) commands | 37 | 1Eh | 7.5 ns 3,CL=6 3,CL=5 2,CL=4 |
| Internal blockage between READ and PRECHARGE (t RTP) commands | 38 | 1Eh | 7.5 ns 3,CL=6 3,CL=5 2,CL=4 |
| Minimum hour per row cycle (t RC) | 41, 40 | 39h, 30h | 57.5 ns 23,CL=6 23,CL=5 15.3, CL=4 |
| Period between self-regeneration commands (t RFC) | 42, 40 | C3h, 30h | 195.0 ns 78,CL=6 78,CL=5 20.8, CL=4 |
| Maximum trivality to the period of the clock signal (t CK max) | 43 | 80h | 8.0 ns |
| SPD revision number | 62 | 12h | Revision 1.2 |
| Identification code of the JEDEC picker | 64-71 | 7Fh, 00h | Qimonda |
| Module Part Number | 73-90 | - | 64T512020EU25FA |
| Module production date | 93-94 | 07h, 48h | 2007 rіk, 48 day |
| Module serial number | 95-98 | 1Ah, 02h, 9h, 14h | 1A029C14h |
The SPD has three values for the signal CAS# - 6, 5 and 4. The first and the other (CL X = 6 і 5) are given the DDR2-800 mode of operation (the hour of the cycle is 2.5 ns, the frequency is 400 MHz) with the identical scheme of the lower timings 5- 5-18 (equally), the third value of the jamming signal CAS# (CL X-1 = 4) validates the DDR2-533 mode (cycle hour 3.75 ns, frequency 266.7 MHz) with a non-standard timing scheme 4-3,33- 3.33-12, the BIOS of most boards will be interpreted as 4-4-4-12.
The revision number of the SPD and the identification code of the compiler are entered correctly, the Part Number matches the one assigned on the modules themselves, and serial number vіdrіznjaєtsya vіd hovered on the stickers.
Support for the SPD extension to the EPP standard in the modules is not extended. Test bench configuration
- Processor: AMD Phenom 9750 (Socket AM2+), 2.4 GHz (200x12), step B3;
- chipset: AMD 790FX;
- motherboard: ASUS M3A32-MVP Deluxe, BIOS version 1201;
- Windows XP SP2 x64.
As a regular mode, we beat the recommendations of the vibrator and the most logical of savings in SPD (DDR2-800 with timings 5-5-5-18). Testing was carried out in two modes of the memory controller in the Phenom processor: ganged (which provides more high productivity in single-threaded access mode) and unganged (more important rich-threaded additives, intensively going to memory). We didn’t go through the development of the potential, wanting to recognize the special talents of these high-capacity modules is hardly reasonable.
| Qimonda DDR2-800 2x4096MB (HYS64T512020EU-25F-A) | Apacer Giant DDR2-1066 2x2048MB | |||||||
| Memory controller mode | Ganged | Unganged | Ganged | Unganged | Ganged | Unganged | ||
| Memory frequency, MHz (DDR2 MHz) | 400 (800) | 400 (800) | 456 (912) | 460 (920) | 400 (800) | 400 (800) |
||
| Processor core frequency, MHz (DDR2 MHz) | 2400 (200x12) | 2400 (200x12) | 2736(228x12) | 2760 (230x12) | 2400 (200x12) | 2400 (200x12) | ||
| CPU memory controller frequency, MHz (DDR2 MHz) | 2000 (200x10) | 2000 (200x10) | 2280 (228x10) | 2300 (230x10) | 2000 (200x10) | 2000 (200x10) | ||
| Timings memory for promotions, voltage | 5-5-5-18-2T, 1.8 V | 5-5-5-18-2T, 1.8 V | 5-5-5-15-2T, 2.3V | 5-5-5-18-2T, 2.3V | 5-5-5-15-2T, 1.8 V | 5-5-5-15-2T, 1.8 V |
||
| Minimal voltage with saving stability, | (Didn't wobble) | (Didn't wobble) | 2.26 V | 2.22V | (Didn't wobble) | (Didn't wobble) | ||
| Average read bandwidth (MB/s), 1 core | 6082 | 5535 | 6938 | 6354 | 6195 | 5760 | ||
| Average write bandwidth (MB/s), 1 core | 3469 | 3459 | 3960 | 3979 | 3548 | 3588 | ||
| Max. Reading bandwidth (MB/s), 1 core | 7014 | 6366 | 8000 | 7306 | 7149 | 6619 | ||
| Max. Write bandwidth (MB/s), 1 core | 4888 | 4953 | 5575 | 5700 | 4965 | 4983 | ||
| Average read bandwidth (MB/s), 4 cores | 10764 | 10715 | 12270 | 12406 | 10960 | 11078 | ||
| Average write bandwidth (MB/s), 4 cores | 3506 | 4965 | 4000 | 5730 | 3550 | 5104 | ||
| Max. Read bandwidth (w/PF, MB/s), 4 cores | 11047 | 10749 | 12594 | 12454 | 11238 | 11105 | ||
| Max. Write bandwidth (NT, MB/s), 4 cores | 6288 | 5604 | 7168 | 7228 | 6315 | 6315 | ||
| Minimal latency of pseudo-vipadal access, ns | 36,4 | 38,8 | 32,0 | 33,9 | 35,7 | 37,0 | ||
| Minimal latency of voice access * ns | 90,1 | 93,3 | 79,0 | 81,1 | 88,2 | 89,5 | ||
* Expand block 32 MB
To match vicorists, a set of smaller modules (2 x 2048 MB) such as Apacer equal frequency(DDR2-800) є, ale minimal. Being respectfully surprised, you can find more information about the security of the recording in the unganged mode of the Qimonda modules.
Although the modules themselves are clearly not addressed to lovers of overclocking, so do not let the radiators and the recommended modes of operation work with increased frequencies and voltage, the overclocking may be possible. And you can more than compensate for the difference in productivity in equal parts with modules of a smaller charge (but, of course, it works at a standard frequency).
Well, in the unganged mode, a stable robot was installed at a higher high frequency, at which it was possible to reduce the voltage by 2.3 V high voltage you can shorten the module service term) up to 2.2 V. Podbags
DDR2 memory modules with a capacity of 4 GB (for a dual-channel configuration with a capacity of 8 GB) have not been exotic for a long time, that price may be unpretentious. Although the most expanded in this category are the modules with the ECC support, there are no redundancies for the segment of working stations, for the purpose of taking such a charge in a standard desktop computer. In every case, the productivity and stability of the looked-up modules in Qimonda turned out to be on top, so you can’t sacrifice the parameters of coristuvachev.
History operational memory, or RAM, began in the distant 1834, when Charles Bebbij developed the "analytical engine" - indeed, the prototype of the computer. Part of the price of the car, yak vydpovidala for the savings of intermediate data, vin calling it a warehouse. The storage of information there was organized in a purely mechanical way, for an additional shaft that gear.
In the first generations of EOM, as RAM, electron-promenev tubes, magnetic drums were victorious, magnetic cores appeared later, and even after them, the third generation of EOM had memory on microcircuits.
Narazі RAM win over technology DRAM form factors DIMM and SO-DIMM, dynamic memory, organized like integrated circuits for heaters. Vaughn is energy-saving, so the data is known for the availability of food.
The choice of operational memory is not foldable for today's day, the smut here is divided into types of memory, recognized by the main characteristics.
Type of memory
SODIMM

SO-DIMM form factor memory is recognized for use in laptops, compact ITX-systems, monoblocks - in a word, there, de important is the minimum physical size of the memory modules. It depends on the DIMM form factor, which is approximately 2 times smaller than the module length, and a smaller number of contacts on the board (204 and 360 contacts for SO-DIMM DDR3 and DDR4 versus 240 and 288 on boards of the same types of DIMM memory).
For other characteristics - frequency, timings, communication, SO-DIMM modules can be different, and DIMMs do not differ in any way.
DIMM
DIMM - random access memory for modern computers.The type of memory, which you will get, in Persh Cherga can be summed up from roses on the mother's board. RAM for the computer is divided into 4 types - DDR, DDR2, DDR3і DDR4.

Memory type DDR appeared in 2001 with 184 contacts. The voltage of life became from 2.2 to 2.4 V. The frequency of the work is 400 MHz. Dosi zustrіchaєtsya at sale, schopravda, the choice is small. For today, the format is out of date, - maybe you don’t want to upgrade the system again, and in the old motherboard, there are only roses for DDR.
The DDR2 standard was already introduced in 2003, having removed 240 contacts, which increased the number of streams, decently speeding up the data transfer bus to the processor. The frequency of the DDR2 robot could become up to 800 MHz (up to 1066 MHz in okremi modes), and the voltage of life from 1.8 to 2.1 was three times less, lower for DDR. Also, the energy supply and thermal imaging of the memory decreased.
DDR2 specifications for DDR:
240 contacts vs 120
· New slot, crazy with DDR
· Lowest energy saving
Improved design, better cooling
Higher maximum operating frequency
So, like DDR, an old type of memory - at the same time, it’s like a old mother’s payment, in other ways there’s no sensation, the new DDR3 and DDR4 shvidsche.
In 2007, the RAM roci were upgraded to the DDR3 type, which can be expanded by mass. Lost your own 240 contacts, but the connection slot for DDR3 became the last one - there is no connectivity with DDR2. The frequency of robotic modules in the middle type is 1333 to 1866 MHz. There are also modules with a frequency of up to 2800 MHz.
DDR3 is similar to DDR2:
· DDR2 and DDR3 slots are insane.
· The clock frequency of DDR3 robots is higher than double - 1600 MHz versus 800 MHz for DDR2.
· Vіdrіznyaєtsya reduced narugozheniya - close to 1.5V, and less energy supply (in the version DDR3L The average value is even lower, close to 1.35).
· Timings (timings) of DDR3 are larger, lower in DDR2, but the working frequency is higher. Zagalom swidkіst roboti DDR3 for 20-30% of the thing.
DDR3 is a good choice these days. For rich motherboards, the sale of roses for DDR3 memory itself, and for the connection with the mass popularity of this type, is unlikely to appear soon. Also vin trohi is cheaper for DDR4.

DDR4 is a new type of RAM, less fragmented in 2012. Evolutionary development of the previous types. The bandwidth of the memory building has been increased again, reaching 25.6 Gb / s. The frequency of the robot also went up - in the middle type 2133 MHz to 3600 MHz. As well as adopting a new type of DDR3, which has entered the market for 8 years and has taken off the mass expansion, then the increase in productivity is insignificant, and far from all motherboards and processors support the new type.
DDR4 specifications:
Inconsistency with previous types
Reduced voltage of life - from 1.2 to 1.05 V, energy supply also decreased
· Working memory frequency up to 3200 MHz (can reach 4166 MHz for some slats), while, obviously, timings, which grew proportionally
· You can change the speed of DDR3 robots
If you already have DDR3 sticks, then hurry up and change them to DDR4 there is no sense. If the format expands massively, and all motherboards support DDR4, the transition to a new type will automatically update the entire system. In this way, you can assume that DDR4 is a better marketing, lower new type of RAM.
What frequency of memory should I choose?
Selecting the frequency needs to be started by rechecking the maximum trimming frequencies by the processor and the motherboard. The frequency is higher boosted by the processor can be taken less for overclocking the processor.On this day, do not select memory with a frequency lower than 1600 MHz. The 1333 MHz option is acceptable for DDR3, as old modules that were not lying around at the seller, as they will obviously be better for new ones.
The best option for today is to store memory with a frequency interval of 1600 to 2400 MHz. The frequency is more likely not to be overwhelmed, but it is much more expensive, and it should be played by modules with increased timings. For example, the difference between modules in 1600 and 2133 MHz in a number of working programs will be no more than 5-8%, in games the difference can be less. Frequencies in 2133-2400 MHz should be taken, so you are engaged in video/audio rendering coding.
The difference between the frequencies of 2400 and 3600 MHz will cost you dearly, without adding much flexibility.
What obsyag operative memory kupuvati?
The volume, which you need, should be kept according to the type of work that is carried out on the computer, according to the installed operating system, according to the programs that are being tested. Also, do not miss out on respect for the maximum support for the memory of your mother's payment.
Volume 2 GB- On today's day, maybe you can get some hiba scho only for revisiting the Internet. More than half za'їdatime operating system, which was left behind to stick to the sloppy robot of non-viable programs
Volume 4 GB- Pіdіyde for a computer of the middle hand, for a home PC-media center. To finish, to watch films, and to play with unseen games. Suchasni - unfortunately, with difficulties. (will be the best choice if you have a 32-bit Windows operating system, so you should have at least 3 GB of RAM)
Volume 8 GB(or a set of 2x4GB) - recommendations were made today for a full-fledged PC. Tsgogo vystachit mayzhe for any іgor, for robots s be-yakim able to resource software. The best choice for a universal computer.
The volume is 16 GB (or sets 2x8GB, 4x4GB) - you will be correct, as you work with graphics, important programming environments, or you can render video consistently. This is also a guide for running online streams - here with 8 GB you can get a boost, especially when high quality video broadcasts. Days of play in high permissions And with HD textures, you can run better with 16 GB of RAM on board.
Volume 32 GB(set 2x16GB, or 4x8GB) - for the time being, it’s still a better choice, you need it for some extreme working tasks. It is better to spend pennies on other components of the computer, it is more important to be listed on yoga code.
Robotic modes: better than 1 memory bar or 2?
RAM can be used in single-channel, two-, three- and four-channel modes. Definitely, since there are enough slots on the motherboard, it would be better to replace one memory bar of the same amount of memory. The speed of access to them is increased from 2 to 4 times.
To remember to pratsyuvala dual channel mode it is necessary to install the strips in the slots of one color on the motherboard. As a rule, the color is repeated through the nest. It is important that the memory frequency of the two planks be the same.
- Single channel mode- Single-channel robotic mode. Vmikaetsya, if one memory bar is installed, or different modules that work at different frequencies. At the result, the memory works at the frequency of the most important bar.
- dual mode- Dual channel mode. Operate less with memory modules of the same frequency, increase the speed of operation by 2 times. Pickers are produced specifically for which set of memory modules, in which there may be 2 or 4 however.
-Triple Mode- Pratsyuє for this very principle, scho th two-channel. Really, don't worry about swidshe.
- Quad mode- Chotiroh-channel mode, which is based on the principle of a two-channel mode, apparently improves the speed of work by 4 times. Vikoristovuєtsya, de need vykljuchno high swidkіst - for example, in the servers.

- Flex Mode- A flexible variant of the two-channel mode of operation, if the bars are of different volume, but the frequency is the same. In this case, in the dual-channel mode, the same connections of the modules will be reversed, and the ones that are left out will function in the single-channel mode.
What do you need to remember the radiator?
At the same time, not for a long time, if, at a voltage of 2 V, the frequency of work was reached at 1600 MHz, and as a result, a lot of heat was seen, as if it were necessary to bring in water. Then the radiator should be a criterion for the survival of the detected module.
In this hour, the energy storage of the memory has been greatly reduced, and the radiator on the module can be correct from a technical point of view, only you can overclock, and the module is practical for you at border frequencies for a new one. At reshti vipadkiv radiators, you can tell the truth, hey, with a beautiful design.

As a massive radiator, and significantly increase the height of the memory bar - this is already a minus, you can put a processor supercooler in the system. Note, to say the least, special low-profile memory modules designed for installation in compact housings. The stench is too expensive for the modules of the great expansion.

What are the timings?
Timings, or latency (latency)- One of the most important characteristics of operational memory, which is used to designate swidcode. We christen zagalny zm_st tsgogo parameter. Simply put, operational memory can be revealed, like a two-world table, in which the middle of the skin carries information. Access to the middle is required for specifying the number of the column and row, and it is required for an additional strobe pulse for access to the row RAS(Row Access Strobe) and strobe CAS (Acess Strobe) change the voltage with a path. In such a rank, for the skin tact, the robots are vibrated RASі CAS, and between these two commands, write / read, there are song stutters, which are called timings.

In the description of the operative memory module, you can add five timings, for clarity, a sequence of digits is written through a hyphen, for example 8-9-9-20-27 .
· tRCD (time of RAS to CAS Delay)- Timing, which defines the delay from the RAS pulse to CAS
· CL (time of CAS Latency)- timing, which determines the delay between the write / read command and the CAS pulse
· tRP (time of Row Precharge)- timing, which determines the stutter during transitions from one row to the next one
· tRAS (time of Active to Precharge Delay)- timing, which determines the delay between the activation of the row and the completion of the work with it; pay attention to the main values
· command rate– assigning a grommet between the command to select the appropriate chip on the module before the command to activate the row; do not specify the timing.

To put it more simply, it is important to know only one thing about timings - what is less, what is better. With this plank, you can use the same frequency of work, different timings, and the module with smaller values will always be the best. Therefore, choose the minimum timings for DDR4, timings of 15-15-15-36 will be a guideline for the average values, for DDR3 - 10-10-10-30. Also, remember that the timings are tied to the frequency of the memory, so when dispersing, better for everything, you will have to increase the timings and timings, and again - you can manually lower the frequency, lowering the timings at the same time. Pay more attention to the consistency of these parameters, choose a better balance, and do not chase after the extreme values of the parameters.
How to get out of the budget?
If you spend more money in your order, you can afford yourself more operational memory. The main difference between cheap and expensive modules will be in timings, frequency of work, and in branding - in house, advertising can cost a lot more expensive for noname modules of an unintelligent picker.In addition, additional pennies to the cost of the radiator, installations on the modules. Far from all slats of wines are needed, but the virobniks do not skimp on them at once.
The price is also stale in terms of timing, which stinks lower than the speed, and obviously, the price.
Otzhe, Mayuchi up to 2000 rubles, You can add a 4 GB memory module, or 2 modules of 2 GB each, which is shorter. Choose according to what the configuration of your PC allows. Modules of DDR3 type can be cheaper than DDR4 ones. For such a budget, it's smarter to take DDR3 yourself.
Before the group up to 4000 rubles includes modules with a volume of 8 GB, as well as a set of 2x4 GB. This is the best choice for any business, professional work with videos, and for any other important environment.

at the bag up to 8000 rubles 16 GB memory will be enough. It is recommended for professional purposes, or for more advanced gamers - check out the reserve, checking for new powerful games.
It's not a problem of vitratiti up to 13000 rubles, then the best choice would be to put them in a set of 4 sticks of 4 GB. For a penny, you can choose a prettier radiator, maybe for a distant dispersal.
More than 16 GB without the need for work in professional important environments (that and then not in all) do not take raja, but if you want to, then for the bag 13000 rubles You can get to Olimp by adding a 32 GB kit or 64 GB. True, for an ordinary koristuvach or a gamer, there will be little sense for anyone - it’s better to spend money, say, on a flagship video card.

Testing high-speed DDR2 modules: what's the point?
If more koristuvachs smell the word "rozgin" or overclocking, then the stench will surely represent zbіlshennya clock frequency processor. But no less important factor is the FSB frequency, which can be easily increased without any problems, ensuring a productivity increase, which is more than a decade of additional MHz on the CPU. The prote for overclocking the components is always obvious, especially in Pentium 4 systems, the decor, for example, is very obvious from the Swedish memory.
In principle, there is nothing importantly filthy in Vikoristan's own memory. The maximum possible frequencies and connection with them are still airborne by the elite modules. For the Athlon 64, tse stands for the alternative DIMM DDR400, which means the ideal CL2-2-2-5 trims.
Current P4 systems use DDR2 RAM. Won zdatna pratsyuvati on more high frequencies ah, lower DDR, that stutter will be painted step by step. Today, the most expanded memory is DDR2-533 (266 MHz), so stepwise change 333-MHz modules (DDR2-667). Most frequencies are currently available only through "rozgіn", although chipset makers are more and more zanurenny in their products.
It would be possible to admit that the greater potential for DDR2 RAM memory overclocking will be transferred to a significant increase in productivity, but, unfortunately, the situation is different in reality. The P4 system with the memory of DDR2-533 appears less than a troch faster than DDR400. That switch to DDR2-667 gave a smaller effect, but it didn't.
At the same time, more and more manufacturers, including A-Data and Corsair, are launching DDR2-667 modules on the market, which can work with low stutters and high frequencies. We took away the modules from both manufacturers and installed them at the "rozignan" P4 system - wonder what happens at DDR2-1066 frequencies.
"Rozgin" in memory of old people

On Intel systems, the RAM bus is always running with a hundred percent FSB frequency. The greater number of modern motherboards give the same flexibility to each other, allowing you to choose more than one factor. Pivnіchny mist chipsetіv 945 and 955x propoût chotir spіvіdnennia frequency: 1:1, 3:4, 3:5 and 2:1. If you take the base FSB frequency of 200 MHz (FSB800) as a basis, you can use DDR2-400, DDR2-533, DDR2-667 and DDR2-800. The remaining option can be done for a long time, but unofficially.
If you want to "split" the system without increasing the memory frequency, move the FSB frequency, switching to a lower coefficient at the same time. Obviously, with what next stitch after it, so that the CPU frequency did not go beyond valid parameters shards won't lie in the FSB frequency. For example, the 3.2 GHz Pentium 4640 is set to 200 MHz FSB by a multiplier of 16. If the FSB frequency reaches 240 MHz, then the CPU will reach 3.84 GHz. It’s not enough for the processors of the building to come into contact with such a frequency.
To take away the DDR2-1066 memory without "overclocking" the system, we changed the ratio to 1:1 (memory bus up to FSB), increasing the FSB frequency to 266 MHz. As a processor, we took a 3.73-GHz Pentium 4 Extreme Edition.

We chose the 3.73-GHz Pentium 4 Extreme Edition, which only works with the FSB frequency of 266 MHz (FSB1066). If the memory bus/FSB 1:1 frequencies are shifted, the memory will work in DDR2-1066 mode.
High frequency or low fading?

AData labels its DIMMs as DDR2-800, while Corsair labels 675 MHz. Have some kind of vipadki pratsyyut tricks CL3-2-2-8.
We protested as low, and great obscurations of memory. As we show our knowledge from the memory of DDR1, it often follows that it works on its own in low winds. For the same reason, AMD announced that the M2 socket and DDR2 memory were not used until CeBIT 2006 - the company's engineers consider the advantages of DDR2 at a frequency of 800 MHz to be insignificant, in order to change the system today.
At the same hour, the memory makers are collapsing at different directions. AData shows that DDR2 DIMMs are built-in at 800 MHz. I next say that this statement is confirmed in practice. But for such frequencies, it is necessary to increase memory obstructions. Corsair went a different way: the top DDR2 memory modules have a maximum frequency of 675 MHz, but with this, the optimal CL3-2-2-8 is given. This allows Corsair to achieve more high productivity, comparable to DDR2-800 modules.
More fatigue, less time to live
Shards of the exchange of technical processes cannot be used to commercially operate 400-MHz chips, the increase in clock frequencies is necessary to increase the power supply. DDR1 modules run at a nominal value of 2.5, so overclockers "disperse" them up to 3.0 V and more. But for DDR2, the base frequency is set to 1.8 V. In principle, 2.0 V for modules is not too high voltage, but higher voltage levels can also be set. Tsya theme sogodnі palko discussed on the forums.
The increase in input voltage increases the memory tolerance, after which it allows you to set more clock frequencies and aggressive fading. But everything has to be paid: the increase in voltage decreases the hour of life of the memory modules.

While AData is taking a stronger position in the US market, it has left Taiwan. The AData product range is similar to other brands and includes many types of SDRAM and flash memory.
On the company's website, you can see different types of DDR2 modules, up to DDR2-1066, if AData live at 1.95 V. However, the DIMMs sent to our laboratory could only reach the DDR2-1066 mode with voltage up to 2.4 B. In view of other varieties, AData products are driven at extremely high frequencies, and the module is certified for 5-cycle CAS fade-out. Although less noise may work, AData does not guarantee it.
We protested against the AData modules, moreover, they installed the stutters manually. In the DDR2-1066 class, 1-GB modules were the most visible, stink shards supported the CL4-5-5-10 stutters. DDR2-800 mode for CL4-4-4-8, DDR2-709 for CL4-3-3-8 and DDR2-533 for CL3-3-3-8.



Corsair guarantees a working frequency of 675 MHz for the modules. We launched the modules in DDR2-1066 mode, but yoga can not be called completely stable. On the view of AData, Corsair chose the minimum stutters: CL3-2-2-8 for DDR2-667 - the best stutters, yak mi zustrichali. In addition, as our tests show, productivity at low trims is often higher, lower at higher clock rates (and higher trims). For the sake of simplicity, the SPD-ROM value is set to CL4-4-4-12. These modules are required on all motherboards. If you want to install large stutters, you should enter them into CMOS yourself.
Corsair modules were ordered in DDR2-800 mode. Although the compiler recommends a voltage of 2.1 for DDR2-667, to avoid CL3-2-2-8 stutters, for DDR2-800 we happened to increase the voltage to 2.2 V. By increasing the voltage to 2.3 V, we could take 533 MHz (DDR2-1066), but the decrease in stability level is no longer improved at different voltage increases. The next sub-chair, which with a frequency of 333 MHz (DDR2-667) and DIMM building, compete with high-frequency competitors.
We chose Corsair DIMMs for our project as the lead through the low end. The Corsair results in our diagrams are assigned to the name of the discriminator, and the results are shown up to the AData DIMM.



Tricks of memory Corsair.
| Processor | |
| Single core CPU | Intel Pentium 4 Processor 660 (3.6 GHz, 2 MB L2 cache) |
| Memory | |
| Intel platform (DDR2-667) | 2x 512 MB - DDR2-667 (333 MHz) Corsair CM2X512A-5400UL (XMS5400 V1.2) (CL3-2-2-8-1T @ 333MHz) 2x 256 MB - DDR2-800 (400 MHz) A-DATA M2OEL6F3G3160A1D0Z (CL4-5-5-10 @ 533 MHz) |
| Motherboard | |
| Intel platform | Gigabyte 8I955X Royal Chipset Intel 955X |
| System hardware security | |
| Graphics card (PCIe) | nVidia Geforce 6800 GT (reference board) GPU: nVidia GeForce 6800 GT (350 MHz) Memory: 256 MB DDR-SDRAM (500 MHz) |
| hard drive | Western Digital WD740 Raptor 74 GB, 8 MB cache, 10000 rpm |
| Merezha | 3Com 3C905B |
| DVD-ROM | Gigabyte GO-D1600C (16x) |
| Living block | Tagan TG480-U01, ATX 2.0, 480 W |
| Software security | |
| Chipset drivers | Intel Inf 7.0.0.1019 |
| Graphics driver | nVidia Forceware 71.84 |
| DirectX | Version: 9.0c (4.09.0000.0904) |
| OS | Windows XP Professional 5.10.2600, Service Pack 2 |

Testi that nalashtuvannya
| Testi that nalashtuvannya OpenGL |
|
| Doom III | Version: 1.0.1262 1280x1024 32 Bit Video Quality = High Quality demo1 Graphics detail = High Quality |
| wolfenstein Enemy Territory |
Version: 2.56 (Patch V 1.02) 1280x1024 32 Bit timedemo1/demo demo4 Geometric detail = high texture detail = high |
| DirectX 9 | |
| Far Cry | Version 1.1 Build 1378 1280x1024 - 32 Bit quality options = High |
| Video | |
| Pinnacle Studio 9 Plus | Version: 9.4.1 from: 352x288 MPEG-2 41 MB to: 720x576 MPEG-2 95 MB Encoding and Transition Rendering to MPEG-2/DVD no Audio |
| Auto Gordian Knot DivX 5.2.1 Xvid 1.0.3 |
Version: 1.95 Audio = AC3 6ch Custom size = 100 MB Resolution settings = Fixed width Codec = XviD and DivX5 Audio = CBR MP3, kbps 192 182 MB VOB MPEG2-source |
| Audio | |
| Lame MP3 | Version 3.97.1 Multi-threaded Alpha Wave 17:14 hvilin (182 MB) to mp3 32 - 320 kbit VBR = rіven 3 |
| Programs | |
| WinRAR | Version 3.40 283 MB, 246 Files Compression = Best Dictionary = 4096 kB |
| 3DS Max 7 | Characters "Dragon_Charater_rig" 1600x1200 Render Single |
| Synthetic | |
| PC Mark 2004 Pro | Version: 1.3.0 CPU and Memory Tests |
| SiSoftware Sandra Pro | Version 2005, SR1 CPU Test = Multimedia Benchmark Memory Test = Bandwidth Benchmark |

Visnovok: the memory of high frequencies is not large
Synthetic testing to give garnu retail between different DDR2 frequencies
Alternately, although the frequencies of AData DIMMs and Corsair are at odds, the performance results are not the same.
As we know, the transition from DDR-533 to DDR2-667 may be more sense for saving low stutters (Corsair). Switching to DDR2-800 gives a minimal increase in productivity, and DDR2-1066, with more stutters, also does not matter. Moreover, the price of shvidkіsnyh modules zovsіm not true increase in productivity, such a stench will be safe.
For business software, installing DDR2 DIMMs is not true for cost reasons, and it is recommended for gamers to spend more pennies on high-end graphic card. In any case, we recommend buying branded memory modules, shards in the house of vibrators give more respect for testing and certification of their products.
As new platforms appear on the mass market, DDR2 memory is gaining more and more popularity, as DDR memory is gradually being removed. The memory of DDR2-400 was no longer enough, but the memory of DDR2-533 came to change quickly. You can now read DDR2-667, DDR2-675, DDR2-750, DDR2-800, DDR2-900, DDR2-1000 memory and type DDR2-1066. With whom it is significant that the standardized memory in a given hour is DDR2-533 and DDR2-667. Soon, DDR2-800 memory will also be standardized, and many motherboards already support this type of memory. Other types of memory are not standardized, and it is not a fact that the motherboard is designed to upgrade memory at the stated clock frequency. Blaming food: why are the memory makers, zmagayutsya one by one, trying to release the daedals more swidkish memory? Vіdpovіd dosit is simple - tse marketing hіd. Age, on the thought of an ordinary purchase, what is the cost of the clock frequency, then shorter. But why is it true that the productivity of the memory is entirely and fully determined by the clock frequency? Is it really necessary today for a fast memory type DDR2-1000, or is it no more than less memory between memory pickers?
It appears that the clock frequency is far from being the only and most important characteristic of memory, which indicates productivity. Where a more important characteristic is memory latency (memory timings), and in the same sense memory DDR2-800 with high latency will be less productive, lower DDR2-667 with low latency.
Vtim, in order to understand all these nuances and understand what latency is and why the characteristic is important for the clock frequency, we need to understand how to work with operational memory.
What is operational memory
Reverse memory (or RAM-memory - Random Access Memory) - memory with sufficient access.
Shards of elementary unity of information are bits, operative memory can be like a set of elementary middles, skin from which one can save one informational bit.
Elementary center of operational memory with a capacitor electric charge, The presence of which can be associated with an information bit. Seemingly simpler, when a logical unit is written to the memory box, the capacitor is charged, and when zero is written, it is discharged. When reading data, the capacitor is discharged through the reading circuit and if the charge of the capacitor is non-zero, then a single value is set at the output of the reading circuit.
Shards of elementary unity of information for modern computersє bytes (bіsіm bіt), then for simplicity, let's take into account that the memory center is elementary, as it can be addressed, taking not a bit, but a byte of information. In this way, access to the memory is viroblyaetsya not bit by bit, but byte by byte.
Microcircuits of memory are organized in a visual matrix, which guesses the arch of the paper in the cell, moreover, the rewriting of the column and the rows of the matrix sets one of the elementary middles. In addition, today's chips of memory make up a sprinkling of banks, the skin of which can be seen as a matrix with its columns and rows.
On fig. 1 shows a simplified scheme of a memory chip, in which there are chotiri cans, skins for 8192 rows and 1024 columns. In this order, the capacity of a skin jar is 8192x1024 = 8192 Kb = 8 Mb. Vrahovyuchi, scho chip and chotiri jars, come out, scho the total capacity of the chip is 32 MB.

When you return to tієї chi іnshoy ї komіrki memory next set the address of the required row and stovptsya.
In order to gain access to the memory compartment for recording or reading information, it is necessary to set the address of the room. Looking at those that have a memory chip on the memory module, and on the skin chip - a bank memory bank, we will need to assign it to the chip and the bank to change the middle. For which vicory there are special signals CS, BA0 and BA1.
The CS signal allows you to select the required memory chip. If the signal is active, access to the memory chip, then the chip is activated. In the other case, the memory chip is inaccessible.
Signals BA0 and BA1 allow addressing one of the two banks in memory. Vrahovyuchi, scho skin signal can accept one of two values: 0 or 1 combinations 00, 01, 10 and 11 allow you to set the address of some banks in memory.
If the chip and memory bank are selected, you can remove access to the required memory box by specifying the address of that row. Row addresses are transmitted behind a special multiplexed address bus MA (Multiplexed Address).
To read the row address, a special strobe pulse RAS (Row Address Strobe) is applied to the input of the memory matrix. To be more precise, this pulse will change the level of the signal from high to low, so that when the RAS signal changes from high to low, it is possible to read the row address.
If so, it is significant that the very reading of the row address is not read at the moment of changing the RAS signal, but is synchronized with the positive edge of the clocked pulse.
Similarly, the reading of the address is taken into account when changing the level of the signal (strobe) CAS # (Column Address Strobe) from a high value to a low value and synchronized with the positive edge of the clock pulse.
To the point, respectfully, that the shards of all memory (reading the address of the row and column, seeing or recording data) are synchronized with the fronts of the clock pulse, the memory is called synchronous.
The RAS# and CAS# impulses are given sequentially one by one, and the CAS# impulse always follows the RAS# impulse, so that the row is selected first, and then the row is selected.
After reading the address of the row and the middle of the memory, it is possible to access it to read or write information. These operations are similar to one to one, but for recording there is a special allowable signal (strobe pulse) WE # (Write Enable). As soon as the signal changes from a high level to a low one due to the voltage, then I will pick up a com- mittee to record the information. Even though the WE# signal is too high, the information is read from the selected room.
Since all data is recorded or read in the middle of the active term, it is necessary to select the Precharge command to close the active row and allow the next row to be activated. Commands that are victorious for writing or reading, and that they become impulsive, that they are presented in the table. 1 and in fig. 2.

Table 1

Memory characteristics
Apparently, the main characteristic of memory is throughput building, so the maximum number of data, as you can improve from memory, or write down a riddle in one hour. The very characteristic is directly and indirectly seen in the name of the type of memory.
In order to signify I will pass the building memory, it is necessary to multiply the system bus frequency by the number of bytes that are transmitted in one clock cycle. SDRAM memory is available on a 64-bit (8-byte) data bus.
For example, DDR400 memory can have a bandwidth of 400 MHz x 8 bytes = 3.2 GB/s. Since memory is used in dual-channel mode, the theoretical memory bandwidth is upgraded, so for DDR400 memory in dual-channel mode it will become 6.4 GB / s. Theoretical building permit for different types memory is shown in the table. 2.

Table 2. Dependence on memory type and theoretical bandwidth
It would have been better if I let the building of memory through more, then better. Partly true, but partly. On the right, the bandwidth of the memory building can be balanced with the bandwidth of the processor bus. And as the bandwidth of the memory building outweighs the bandwidth of the processor bus, the processor bus itself becomes a bottleneck in the system, surrounding the memory capacity. How to look at the Intel Pentium 4 processor or the new dual core Intel processors Pentium D, clock frequency of the processor bus becomes 800 or 1066 MHz. It is safe to change the bus width to 64 bits (or 8 bytes), it is necessary to change the bandwidth of the processor bus to 6.4 or 8.5 GB / s. Why is it obvious that in the system there is a processor with an FSB frequency of 800 MHz, then in single-channel mode for a balanced version, DDR2-800 memory is sufficient, and in dual-channel mode - DDR2-400.
In a similar way, as in the system there is a processor with an FSB frequency of 1066 MHz, then in single-channel mode for a balanced solution it is necessary to chip DDR2-1066 memory, and in dual-channel mode - enough DDR2-533 memory.
Looking at those that are typical for dual-channel mode memory, DDR2-533 memory is a completely balanced solution.
Power supply fault: if the DDR2-533 memory ensures the throughput of the building, what is the use of the bandwidth of the processor bus, do you need more swidcode memory? On the right, in the fact that the dosі mi spoke only about the theoretical, about the maximum possible throughput of the building, as it is realized less in successive transmission of data - if the data is transmitted with skin tact. In a real situation, the theoretical boundary is unattainable, shards, of course, it is necessary to protect and tact, as it is necessary to deny access to the memory compartment itself, as well as to build a memory module. In connection with other important characteristics, memory timings or latency.
Under the latency, it was accepted to understand the delay between the necessary commands and the implementation. This sensory latency can be matched with a telephone ring. The hour that passes after dialing the number (subscriber's call) and until the end of the call in the tube, the cost and the latency of the telephone call.
Memory latency, which is defined by timings, is the same stutters, which are vibrated by a number of beats, between other teams. Let's look at the timings in memory of the report. On fig. 3 shows the sequence of commands for an hour of reading or writing data for a riddle. Activation of the required memory row (ACTIVE command) is prompted, then the RAS signal is changed to a low level and the address of the row is read. Next, follow the command to write (WRITE) or read (READ) data, for which the CAS signal is transferred to a low level and the WE signal is set to a high level. When CAS is set to a low level, after the arrival of a positive front of the clock pulse, the selection of the address is set, which is currently on the address bus, and access to the required memory matrix is enabled. However, the read or write command cannot be followed directly by the activation command - it is necessary between the two commands, so that between the RAS and CAS pulses, after the first RAS to CAS Delay (jamming the CAS signal and the RAS signal). Qiu zatrimku, yak vymіryuєtsya in cycles of the system bus, it is accepted to designate tRCD.

After the command to read (write) data to see the first element of data on the bus (write data to the memory card), pass an hour, which is called CAS Latency. Tsya zatrimka vymіryuєtsya at the cycles of the system bus and is indicated by tCL. The skin of the attacking element of the tributes is settled on the tires of the tributes at the black tact.
The completion of the cycle of loading to the memory bank is caused by the issuance of the PRECHARGE command, which will bring the memory row to close. After the PRECHARGE command, until a new memory row activation command arrives, it may take an hour (tRP), Row Precharge ranks.
Another type of delay, ranks ACTIVE to PRECHARGE delay, is an interval of an hour between the memory row activation command and the PRECHARGE command. Tsya zatrimka is indicated by tRAS and is controlled by the clocks of the system bus.
Well, the last type of zatrimka, which is necessary to guess, is the speed of the command rate. Command Rate is the delay in system bus cycles between the CS# command, the chip selection and the row activation command. As a rule, the Command Rate is set to one or two cycles (1T or 2T).
Jam descriptions - RAS to CAS Delay (tRCD), CAS Latency (tCL) and Row Precharge (tRP) - define memory timings that are recorded in the tCL-tRCD-tRP-tRAS-Command Rate sequence. For example, for the DDR400 (PC3200) module, the timings can be as follows: 2-3-4-5-(1T). This means to set CAS Latency (tCL) to 2 clocks for this module, RAS to CAS Delay (tRCD) to 3 clocks, Row Precharge (tRP) to 4 clocks, ACTIVE to PRECHARGE delay (tRAS) to 5 clocks and Command Rate to 1 beat.
I realized that the less timings, the more memory. To that, if you compare memory with timing 3-3-3-5-(1T) and memory with timing 3-2-2-5-(1T), then the rest will show more swidcode.
Memory SDR
Having sorted out such important characteristics of memory, like timings, you can go directly to the principles of working memory. Regardless of those that this article is dedicated to modern DDR2 memory, a look at the principles of memory operation is mostly based on SDRAM type SDR (Single Data Rate) synchronous memory.
SDR SDRAM-memory ensures synchronization of all input and output signals with the positive edges of the clock generator pulses. The entire memory array of the SDRAM module is divided into two independent banks. This decision allows you to send a selection of data from one bank from the set address to another bank, then immediately mother two open side. Access to these sides is cherguetsya (bank interleaving) and obstructions are gradually fixed, which ensures the creation of an uninterrupted flow of data.
The most widely used types of SDRAM memory until recently were PC100 and PC133. The numbers 100 and 133 indicate the frequency of the system bus in megahertz (MHz) to support the memory. In terms of internal architecture, control methods and external design, the PC100 and PC133 memory modules are identical.
SDRAM-memory has organized package not processed data, which allows you to send a call to a new address in the middle of the memory of the skin clock cycle. SDRAM microcircuits have a name for increasing the address of the middle memory stovptsіv, schob secure easy access to them.
In SDRAM-memory, the core and exchange buffer work in synchronous mode at the same frequency (100 or 133 MHz). The transfer of the skin bit from the buffer is controlled by the skin clock of the memory core.
The timing diagram of SDR SDRAM memory is shown in fig. four.

DDR memory
Am'yat DDR SDRAM, so I came to change the memory of SDR, secure more bandwidth in the building. The abbreviation DDR (Double Data Rate) at the name of the memory means a double data transmission speed. In DDR-memory, the buffer I/O transfers two bits per clock cycle, which actually works at a subclock frequency, overflowing with the synchronization with the memory core. Such a mode of work is possible for the patient, as it is only two bits available to the output buffer on the skin cycle of robotic memory. For whatever it is necessary, the skin command to read resulted in the transfer of a two-bit buffer from the memory core. In this way, two independent lines of transmission from the memory core to the buffers for output-to-video output are selected, the sounds are sent to the data bus in the required order.
With this method of organizing robotic memory, two bits are prefetched before being transferred to the data bus, which is also called Pre-fetch 2 (prefetch 2).
In order to create synchronization between the robotic memory core and input-output buffers, the same clock frequency is beaten (one and the same clock pulses). Just as at the very core of the memory, synchronization occurs behind the positive front of the clock pulse, then in the input-output buffer for synchronization, both the positive and negative front of the clock pulse are vibrated (Fig. 5). In this way, the transfer of two bits from the buffer to the I/O buffer along two separate lines is behind the positive edge of the clocking pulse, and their transmission to the data bus is both behind the positive and behind the negative edge of the clocking pulse. Tse secure vdvіchі more high speed buffer operation and higher memory throughput (div. Fig. 5).

All other important characteristics of the DDR-memory have not changed: the structure of many independent banks allows you to select data from one bank and set the address to another bank, so that you can simultaneously check two sides. Access to tsikh storіnok cherguєtsya (bank interleaving), scho lead to usunennya zatrimok that secure creation of an uninterrupted flow of data.
DDR2 memory
In order to follow the terminology of SDR (Single Data Rate), DDR (Double Data Rate), it would be logical to call the DDR2 memory QDR (Quadra Data Rate), but this standard can be used on the other hand, and there is more speed of transmission than in the DDR2 standard with burst mode access, data is transmitted several times per cycle. For organization given to the regime It is necessary to work with the memory, so that the input-review buffer is processed at the same frequency as the frequency of the memory core. It is reached as follows: the core of the memory, like before, is synchronized along the positive front of the clocking impulses, and with the arrival of the skin positive front, along four independent lines, the input-to-vod buffer is transmitted to the input-to-vod buffer with some information (more than one beat per clock). The I/O buffer itself is clocked at the sub-frequency of the memory core and is synchronized both behind the positive and behind the negative edge of the frequency. In other words, with the advent of positive and negative fronts, the transmission of battles in the multiplex mode to the data bus (Fig. 6) occurs. Tse allows for the skin cycle of the robotic core of the memory to transfer chotiri beats to the data bus, so that four times increase the bandwidth of the memory building.

In case of DDR memory, DDR2 memory allows to provide the same throughput building, but with a lower core frequency. For example, DDR400 memory core operates at 200 MHz, and DDR2-400 memory operates at 100 MHz. For this sensor, DDR2 memory can significantly increase the potential for increased bandwidth over DDR memory.
From theory to practice: DDR2-667 memory Kingmax KLCD48F-A8EB5-ECAS
vivchivshi theoretical aspects of the functioning of the current DDR2 memory, let's move on from theory to practice. Like a butt we can see new memory SDRAM DDR2-667 from Kingmax. Stand for testing maw the following configuration:
- Processor: Intel Pentium 4570 (clock speed 3.8 GHz, L2 cache 1 MB);
- FSB frequency: 800 MHz;
- motherboard: MSI P4N Diamond;
- chipset: NVIDIA nForce4 SLI Intel Edition;
- memory: two DDR2-667 Kingmax KLCD48F-A8EB5-ECAS modules with a capacity of 1 GB leather each (dual-channel robot mode);
- video card: MSI NX6800 Ultra-T2D512E.
Unfortunately technical information about the Kingmax KLCD48F-A8EB5-ECAS modules on the website of the picker. The only thing to know about the organization of the module (8X128 MB) and about the value of the CAS Latency parameter is to set 5 cycles.

For memory testing, we tested the RightMark Memory Analyzer v 3.55 test package and a set of gaming benchmarks: Half-Life 2, DOOM 3, FarCry 1.3, Unreal Tournament 2004 and 3DMark 2003. The video card driver has been adjusted to maximum performance.
As it happened during the testing process, the memory modules KLCD48F-A8EB5-ECAS can perform timings for locking (by SPD) and set the sequence 5-5-5-13-(2T). In this manner:
CAS Latency (tCL) - 5T;
RAS to CAS delay (tRCD) - 5T;
Row Precharge (tRP) - 5T;
Active to Precharge (tRAS) - 13T;
Command Rate - 2T.
In order to evaluate the capacity of the memory modules for overclocking (albeit without shkoda for stability), we also conducted tests in the modes with the lowest timings, which were determined by the pardon test method. As it turned out, the minimum timings that trim these memory modules at a clock frequency of 667 MHz, set the sequence 4-3-3-5-(2T). In addition, we carried out a memory breakdown with a clock frequency in order to evaluate the maximum possible clock frequency, supported by these modules when operating in dual-channel mode.
For testing with the benchmarks of the RightMark Memory Analyzer v 3.55 test package, the following presets were included in the benchmark:
RAM Performance Stream
Average Memory Bandwidth, SSE2;
Maximal RAM Bandwidth, Software Prefetch, SSE2;
Average RAM Latency;
Minimal RAM Latency, 16 Mbyte Block, L1 Cache line.
W report description skin preset can be found at www.rightmark.org or www.ixbt.com.
The results of testing for the auxiliary test package RightMark Memory Analyzer v 3.55 are presented in Table. 3.

with references to the test package RightMark Memory Analyzer v 3.55
Depending on the results of testing, timings for closing (by SPD) are highly dependent. The change in timing does not affect the stability of the robotic memory modules, it will only lead to a significant increase in memory throughput and a decrease in latency. So, the maximum memory bandwidth with timings 5-5-5-13-(2T) becomes 5967.3 MB / s (read operation, Maximal RAM Bandwidth preset, Software Prefetch, SSE2). At that very hour, when the timings are changed to 4-3-3-5-(2T), the bandwidth will increase to 6294.9 MB / s, which is 5.5%. Significantly, the value of 6294.9 MB / s is close to the theoretical bandwidth of the processor bus, as in to this particular type stores 6.4 GB/s.
An increase in clock frequency up to 710 MHz does not affect the stability of robotic memory, but in order to achieve a significant increase in memory productivity, it does not go into this case, which once again confirms the fact that changing the timing of memory significantly affects productivity , lower clock frequency increase .
Now we're looking forward to the results of the game tests (Table 4). Just like that, changing the timing in memory allows (even if it's a little bit) to improve the results of all game tests. At that very hour, the increase in the clock frequency of the memory does not appear on the test results.

***
Also, as we are talking about the examined Kingmax KLCD48F-A8EB5-ECAS memory modules, we can state that in the mother MSI board P4N Diamond, and also, with the NVIDIA nForce4 SLI Intel Edition chipset, these modules guarantee stable operation and miraculously change timings. To that end, we have decided to give the Kingmax KLCD48F-A8EB5-ECAS modules the “Editorial Recommended” mark.
Editorial board under Kingmax( www.kingmax.com )for the addition of Kingmax KLCD48F-A8EB5-ECAS memory modules.
Publication date:
25.06.2009
As you can see, operative memory contributes to a large storage capacity of a computer's productivity. I realized that coristuvachi try to increase their operational memory to the maximum.
For example, 2-3 years ago, there were literally a few types of memory modules on the market, then at once there are significantly more of them. And it became more comfortable for them to get along.
In these articles, we can see the difference in the marking of memory modules, so that it is easier for you to navigate in them.
For the beginning, we introduce a number of terms, which we need to understand the article:
- bar ("dice") - memory module, paid fee with memory chips on board, which are installed at the memory slot;
- a one-sided bar - a memory bar, which has a memory microcircuit zapped from one side of the module.
- a double-sided bar - a memory bar, so that memory microcircuits can be expanded on both sides of the module.
- RAM (Random Access Memory, RAM) - memory with sufficient access, it seems simpler - operational memory. This is an energy-saving memory, instead of being used for daily life.
- SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM) - synchronous dynamic random access memory: all current memory modules can itself be such an attachment, so that they require constant synchronization and updating instead.
Clearly marked
- 4096Mb (2x2048Mb) DIMM DDR2 PC2-8500 Corsair XMS2 C5 BOX
- 1024Mb SO-DIMM DDR2 PC6400 OCZ OCZ2M8001G (5-5-5-15) Retail
About `em
The first signs in a row were covered by memory modules. Zokrema, the first vipad has 4 GB, and the other has 1 GB. Truthfully, 4 GB is implemented not with one memory bar, but with two. So the titles of Kit of 2 are a set of two planks. Sound like this and the kits are used to install strips in the dual-channel mode in the parallel slot. The fact that they can have the same parameters, to improve their confusion, which is pleasantly signified on stability.
Enclosure type
DIMM/SO-DIMM is the same type of memory strip housing. All modern memory modules are available for one of the two designations of the constructive vikonan.
DIMM(Dual In-line Memory Module) - a module, which has contacts lined up in a row on both sides of the module.
DDR SDRAM memory is available in 184-pin DIMMs, while DDR2 SDRAM memory is available in 240-pin brackets.
Notebooks have smaller memory modules. SODIMM(Small Outline DIMM).
Memory type
Memory type - the architecture that organizes the memory microcircuits themselves. Vaughn pours on everything technical characteristics memory - productivity, frequency, food intake and other.
At the moment there are 3 types of memory: DDR SDRAM, DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM. Of these, DDR3 is the most productive, which saves the least energy.
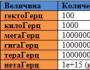
Transmission frequencies for memory types:
- DDR: 200-400MHz
- DDR2: 533-1200MHz
- DDR3: 800-2400 MHz
The figure, which is indicated after the type of memory - i є frequency: DDR400, DDR2-800.
Memory modules of all types are held in place by an elastic life and roses and do not allow to be inserted one into one.
The transmission frequency characterizes the potential of the memory bus for data transmission per hour: the higher the frequency, the more data can be transmitted.
However, there are other factors, such as the number of memory channels, the size of the memory bus. The stench also injects into the productivity of memory subsystems.
For a comprehensive assessment of the capacity of RAM, the term memory capacity is used. Vіn vrakhovuє i frequency, on which data is transmitted, that tire capacity and the number of memory channels.
Bandwidth (B) = Frequency (f) x memory bus width (c) x channels (k)
For example, with a different DDR400 400 MHz memory, that dual-channel memory controller will have:
(400 MHz x 64 bits x 2)/8 bits = 6400 MB/s
On 8 mi, they filed, to transfer Mb / s Mb / s (in 1 byte 8 bits).
Memory Module Width Standard
In order to facilitate the understanding of the speed of the module, the memory bandwidth standard must be specified. Vіn i show, yaku pass building maє module.
All these standards start with the letters PC and give numbers that indicate the memory bandwidth in Mbytes per second.
| Module name | Bus frequency | Chip type | |
| PC2-3200 | 200 MHz | DDR2-400 | 3200 MB/s or 3.2 GB/s |
| PC2-4200 | 266 MHz | DDR2-533 | 4200 MB/s or 4.2 GB/s |
| PC2-5300 | 333 MHz | DDR2-667 | 5300 MB/s or 5.3 GB/s 1 |
| PC2-5400 | 337 MHz | DDR2-675 | 5400 MB/s or 5.4 GB/s |
| PC2-5600 | 350 MHz | DDR2-700 | 5600 MB/s or 5.6 GB/s |
| PC2-5700 | 355 MHz | DDR2-711 | 5700 MB/s or 5.7 GB/s |
| PC2-6000 | 375 MHz | DDR2-750 | 6000 MB/s chi 6.0 GB/s |
| PC2-6400 | 400 MHz | DDR2-800 | 6400 MB/s or 6.4 GB/s |
| PC2-7100 | 444 MHz | DDR2-888 | 7100 MB/s or 7.1 GB/s |
| PC2-7200 | 450 MHz | DDR2-900 | 7200 MB/s or 7.2 GB/s |
| PC2-8000 | 500 MHz | DDR2-1000 | 8000 MB/s or 8.0 GB/s |
| PC2-8500 | 533 MHz | DDR2-1066 | 8500 MB/s or 8.5 GB/s |
| PC2-9200 | 575 MHz | DDR2-1150 | 9200 MB/s or 9.2 GB/s |
| PC2-9600 | 600 MHz | DDR2-1200 | 9600 MB/s or 9.6 GB/s |
| Memory type | Memory frequency | Hour cycle | Bus frequency | Data transfer per second | Naming the standard | Peak speed of data transmission |
| DDR3-800 | 100 MHz | 10.00 ns | 400 MHz | 800 million | PC3-6400 | 6400 MB/s |
| DDR3-1066 | 133 MHz | 7.50 ns | 533 MHz | 1066 million | PC3-8500 | 8533 MB/s |
| DDR3-1333 | 166 MHz | 6.00 ns | 667 MHz | 1333 million | PC3-10600 | 10667 MB/s |
| DDR3-1600 | 200 MHz | 5.00 ns | 800 MHz | 1600 million | PC3-12800 | 12800 MB/s |
| DDR3-1800 | 225 MHz | 4.44 ns | 900 MHz | 1800 million | PC3-14400 | 14400 MB/s |
| DDR3-2000 | 250 MHz | 4.00 ns | 1000 MHz | 2000 million | PC3-16000 | 16000 MB/s |
| DDR3-2133 | 266 MHz | 3.75 ns | 1066 MHz | 2133 million | PC3-17000 | 17066 MB/s |
| DDR3-2400 | 300 MHz | 3.33 ns | 1200 MHz | 2400 million | PC3-19200 | 19200 MB/s |
The tables indicate the peak values themselves, in practice the stench can be inaccessible.
Virobnik ta yoga part number
Leather maker for your skin product, or details give some internal marking, as it is called P / N (part number) - part number.
For the memory modules of other manufacturers, it looks something like this:
- Kingston KVR800D2N6/1G
- OCZ OCZ2M8001G
- Corsair XMS2 CM2X1024-6400C5
On the site of rich collections in memory, you can check how the Part Number is read.
Modules Kingston ValueRAM families:
Kingston modules of the HyperX family (with additional passive cooling for overclocking):
Behind the OCZ markings, you can understand that this is a DDR2 module with a volume of 1 GB, a frequency of 800 MHz.
For marking CM2X1024-6400C5 Apparently, the 1024 MB DDR2 module complies with the PC2-6400 standard and CL=5.
Deyakі robniki zamіst frequency аbo standard memіyatі specify the hour for ns access to the chip memory. For the whole hour you can understand how the frequency is victorious.
So to rob Micron: MT47H128M16HG-3. The number in the end means that the hour of access is 3 ns (0.003 ms).
Behind the forum T=1/f robotic chip frequency f=1/T: 1/0.003 = 333 MHz.
Transmission frequency is 2 times higher - 667 MHz.
Obviously, this module is DDR2-667.
Timings
Timings - these are stutters when turning to memory chips. Zvichayno, scho stink less - tim svidshe pratsyuє module.
On the right, in that the memory chips on the modules create a matrix structure - they are represented in the middle of the matrix with the row number and the column number.
When you remember until the middle of the memory, the whole row is read, in which the necessary middle is known.
On the back, choose the choice of the required row, then the required row. On the edge of the row and the number of the column there is a necessary middle. With the blessings of the grandeur of today's RAM, such matrices of memory are not a whole - for more swedish access until the middle of my memory, the stink of the stench was broken on the sides of that bank.
On the back, we move forward to the bank of memory, activate the side in the new, then we move the robot between the flow side: choose a row and a column.
All tsі diї vіdbuvaєs z insanely obscure like one of one.
Basic RAM timings - there is a delay between the submission of the row number and the number of the column, as it is called the hour of full access ( RAS to CAS delay, RCD); CAS latency, CL), zatrimka between reading the rest of the middle and giving the number of the new row ( RAS precharge, RP). Timings are reduced in nanoseconds (ns).
Timings so and go one by one in the order of the last operations and are also indicated schematically 5-5-5-15 . In this case, all three timings are 5 ns each, and the full working cycle is 15 ns from the moment the row is activated.
Important timing is important CAS latency, which is often abbreviated CL=5. The very best "galmue" memory.
Based on this information, you can correctly select the required memory module.